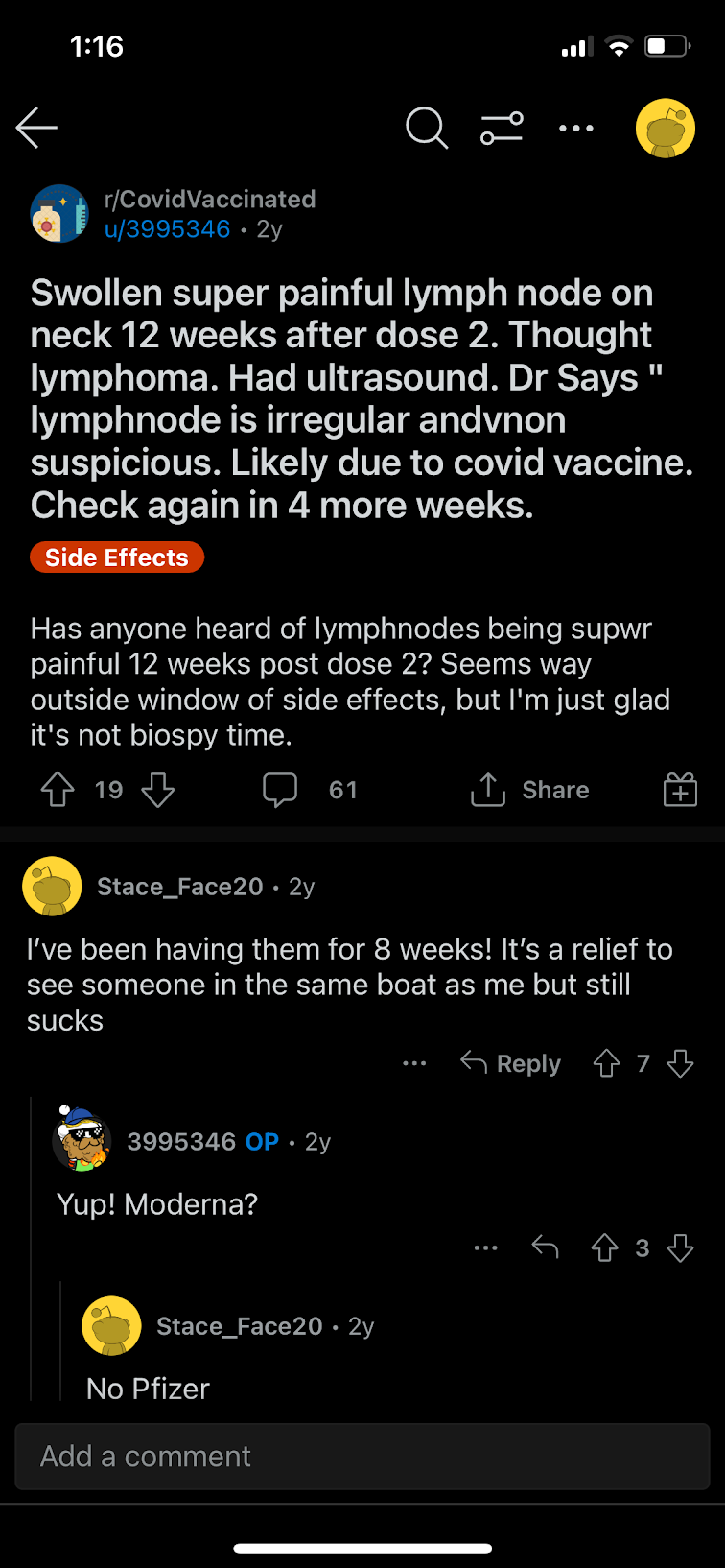
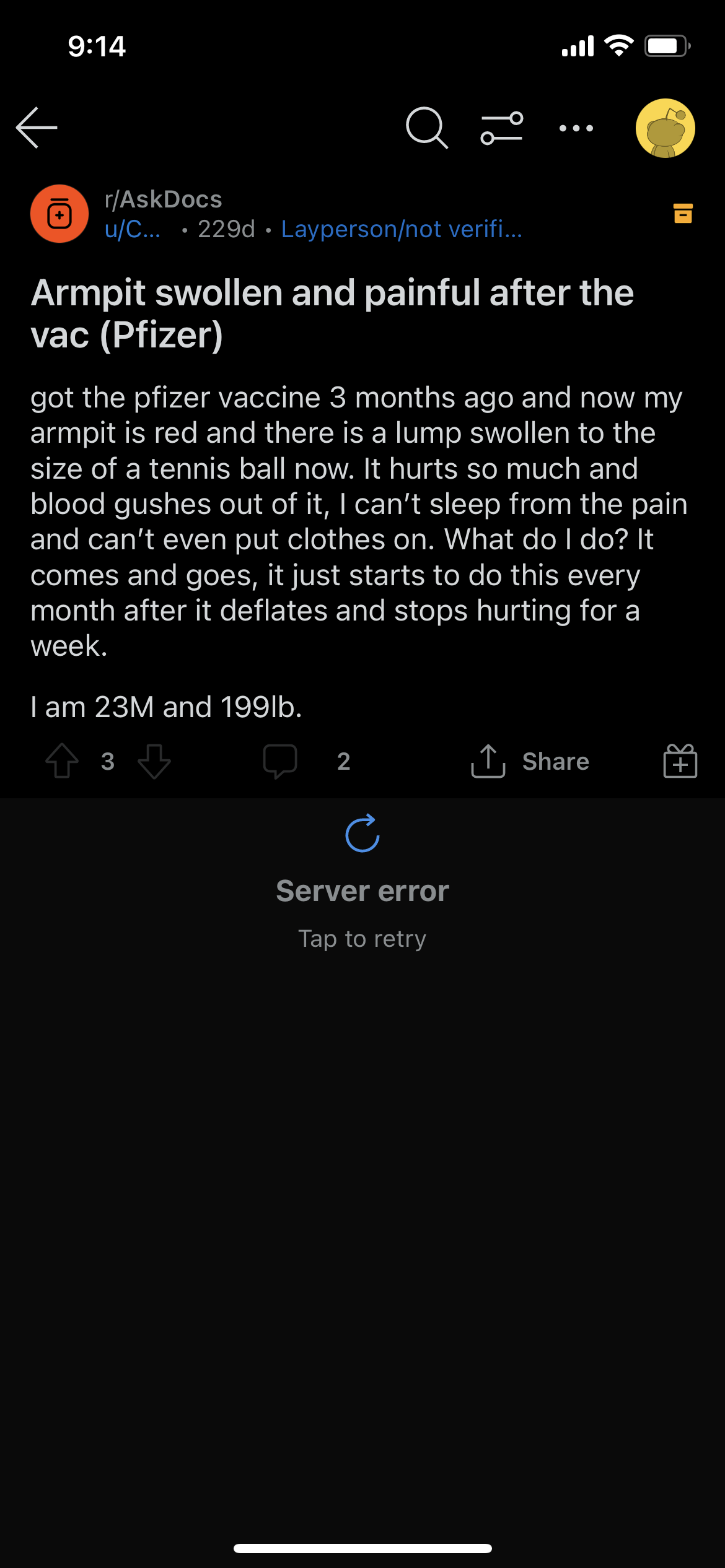
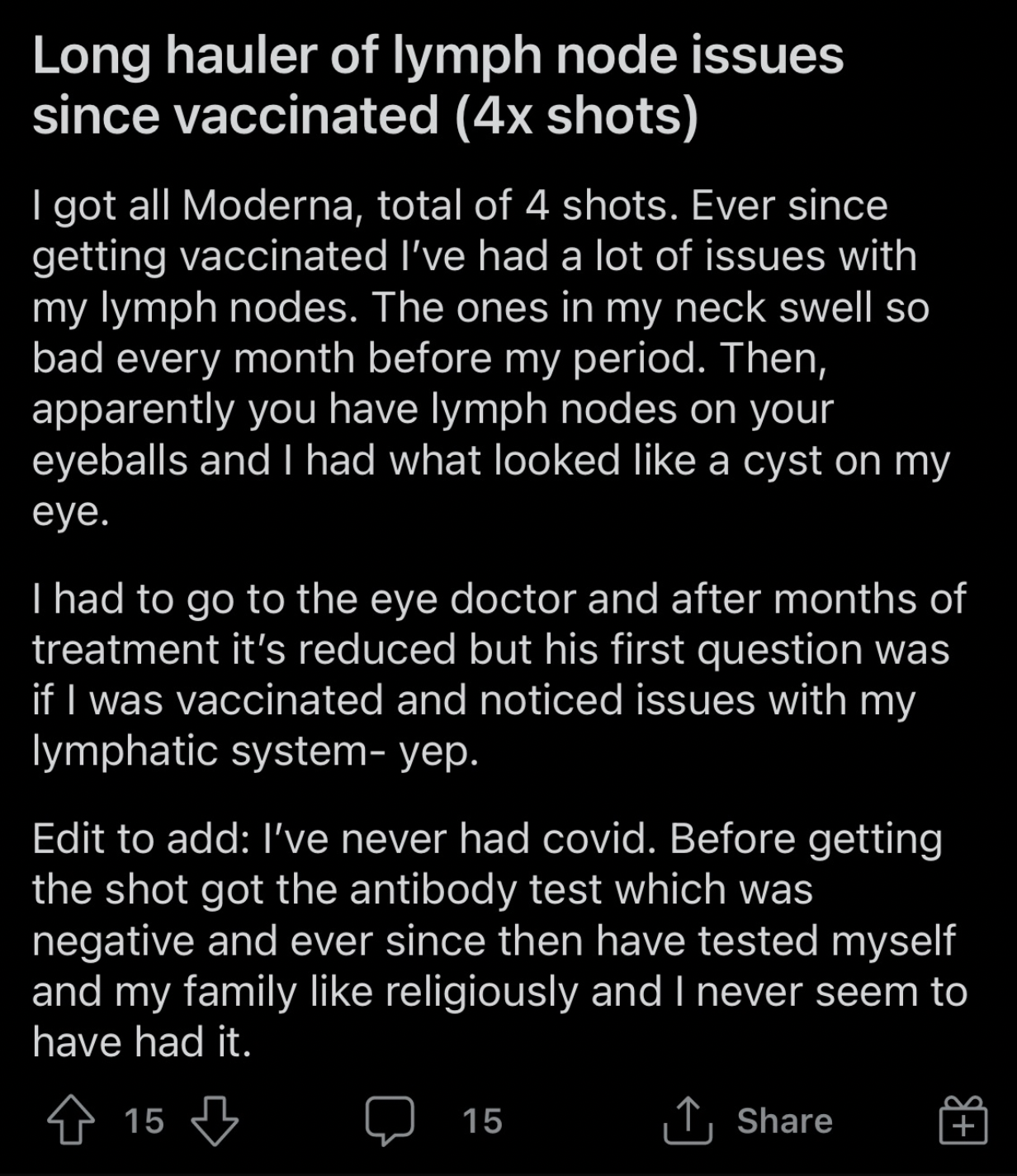
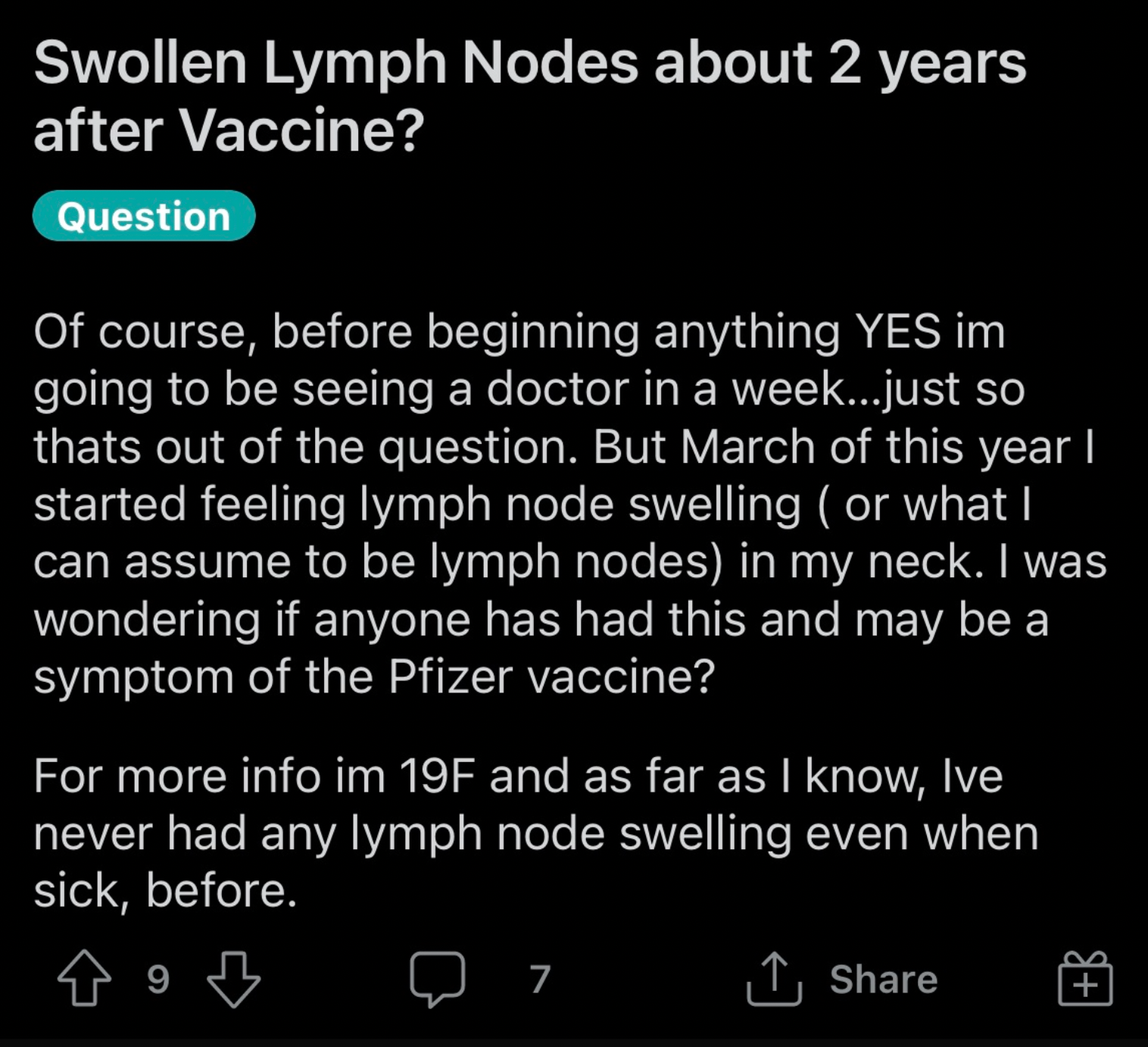
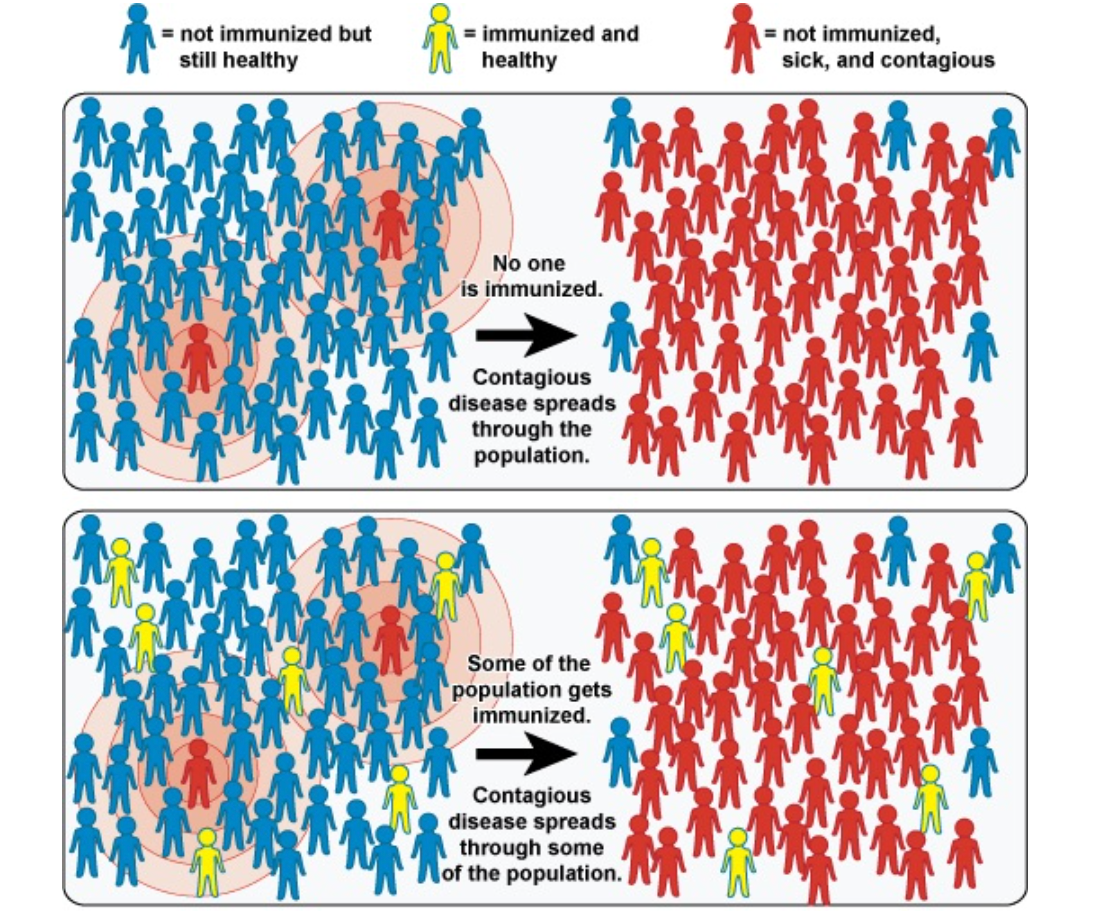
The lymphatic system is the part of the immune system that acts as a strategic filter and vessel with the circulatory system - providing a location for the yuck to accumulate, and allowing the body to create soldiers against the yuck.
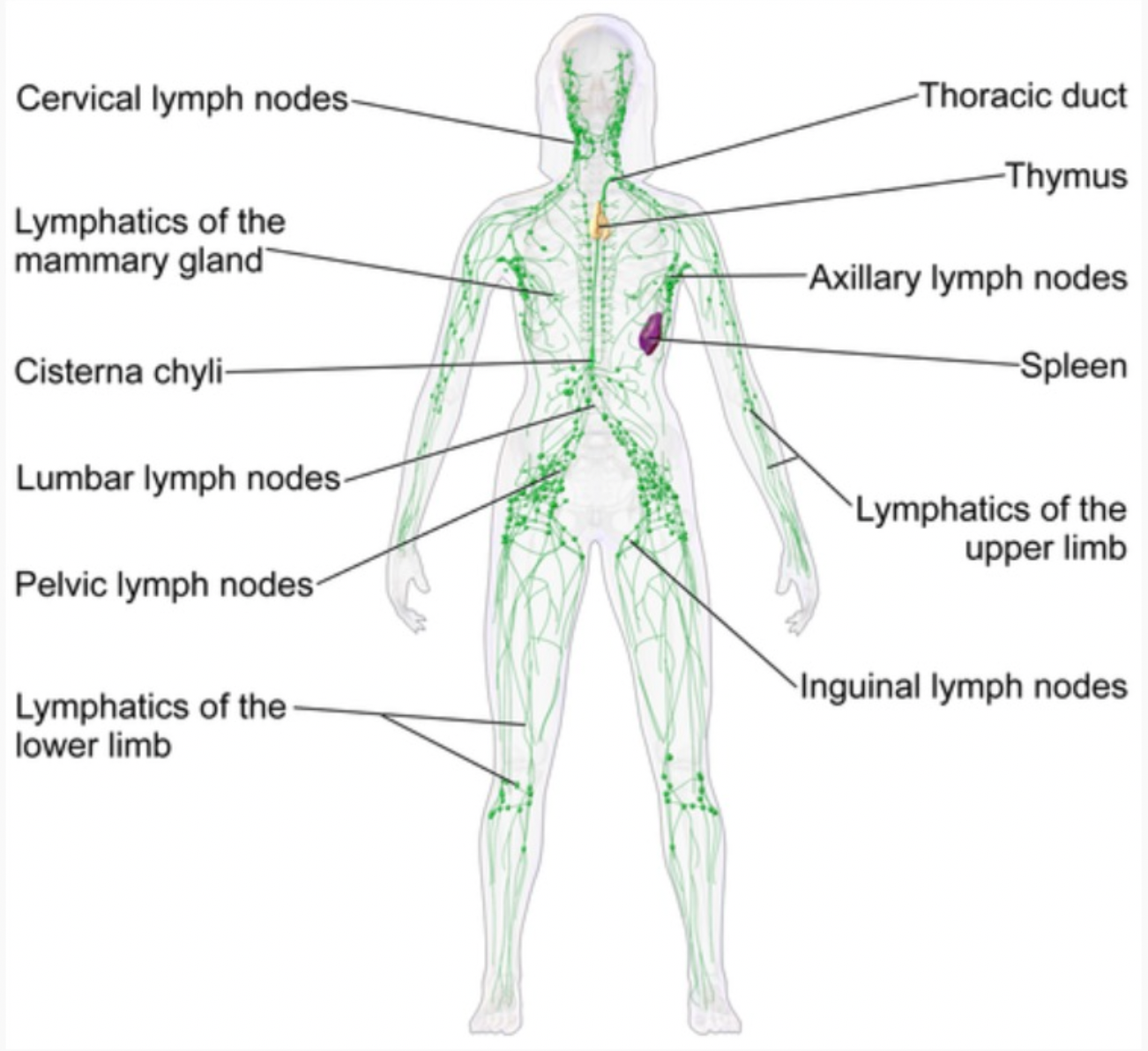
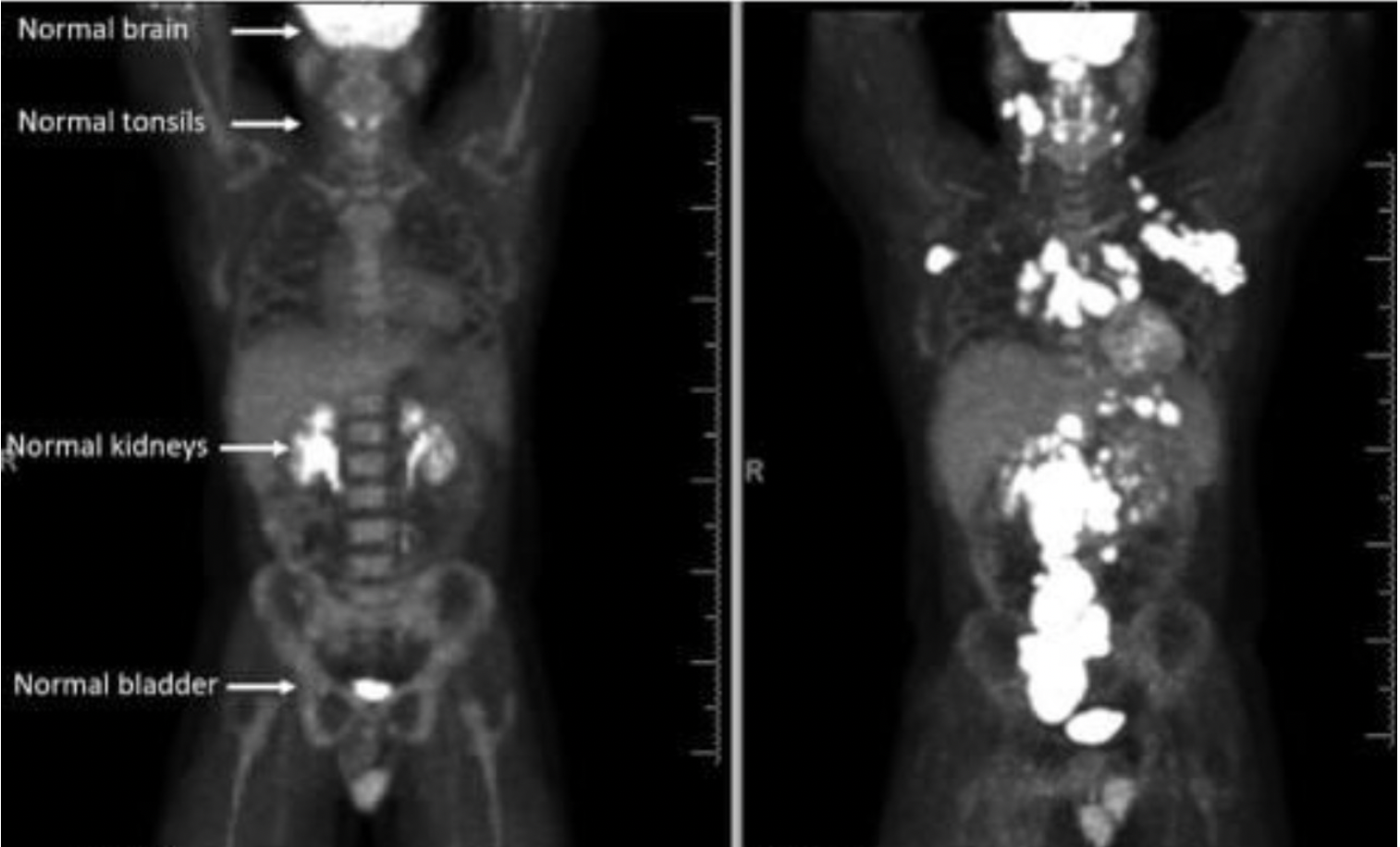
Lymphoma occurs when there's an overwhelming accumulation in the lymph node. This can build up and cause severe infection, sepsis or can grow cancerous over time.

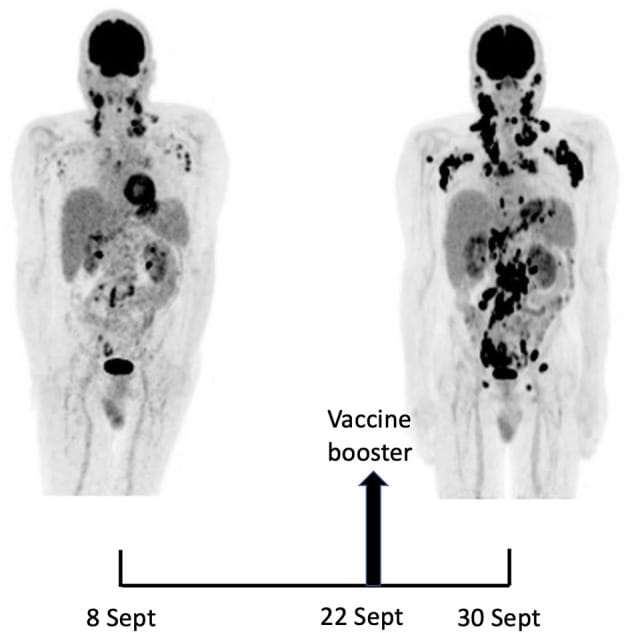
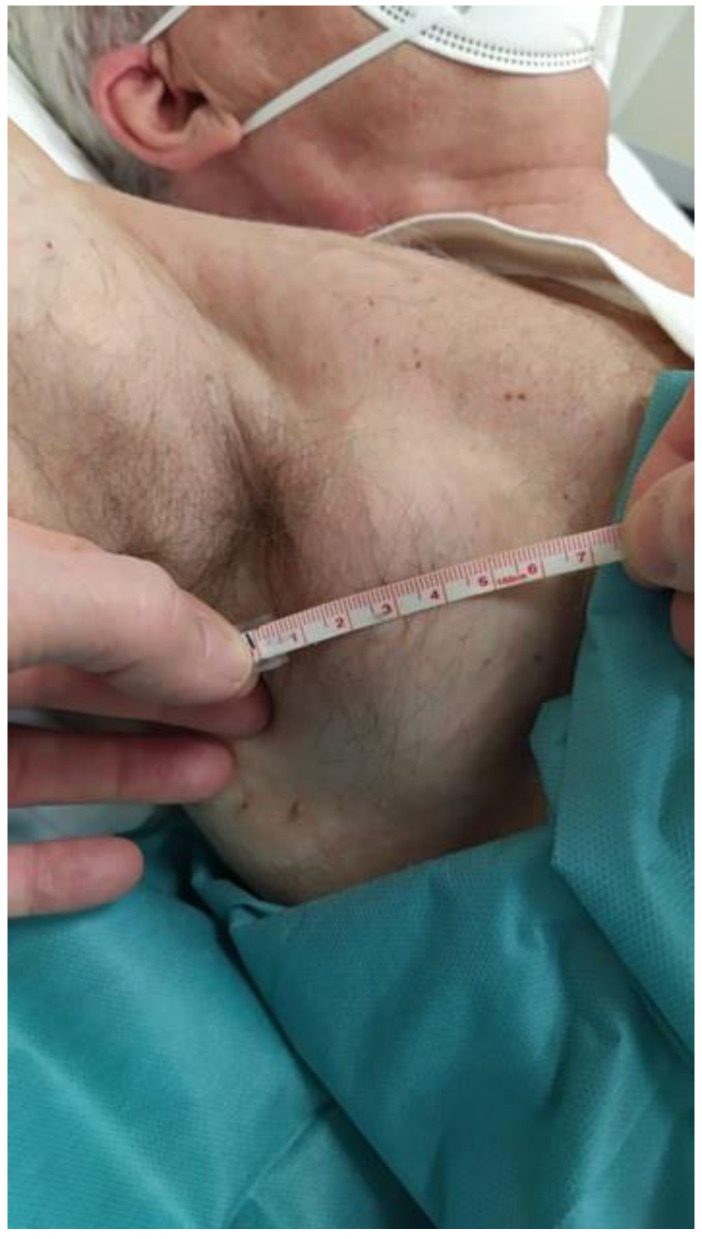
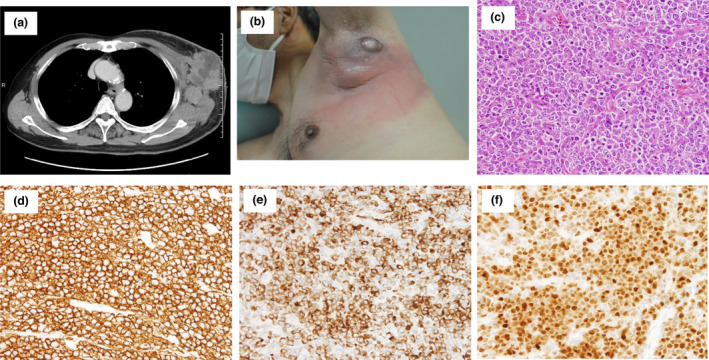

So logically, if a bunch of your cells were producing spike proteins with no off switch until they die, and by the way these spike proteins are for a non-existent but possible danger, the spike proteins could accumulate faster than the body is able to break them down and flush them out.
In a normal immune system, lymph nodes will reach a tipping point and call clean house, triggering a fever and symptoms the body will use to help clear everything out. When the immune system goes into full attack, it produces acute symptoms that usually last 7 to 14 days, sometimes 21.
The immune system is powered by your circadian rhythm and it functions in cycles of 7. But with vaccination, your immune system can't mount an acute response - by dulling the symptoms we actually disadvantage our bodies natural function.





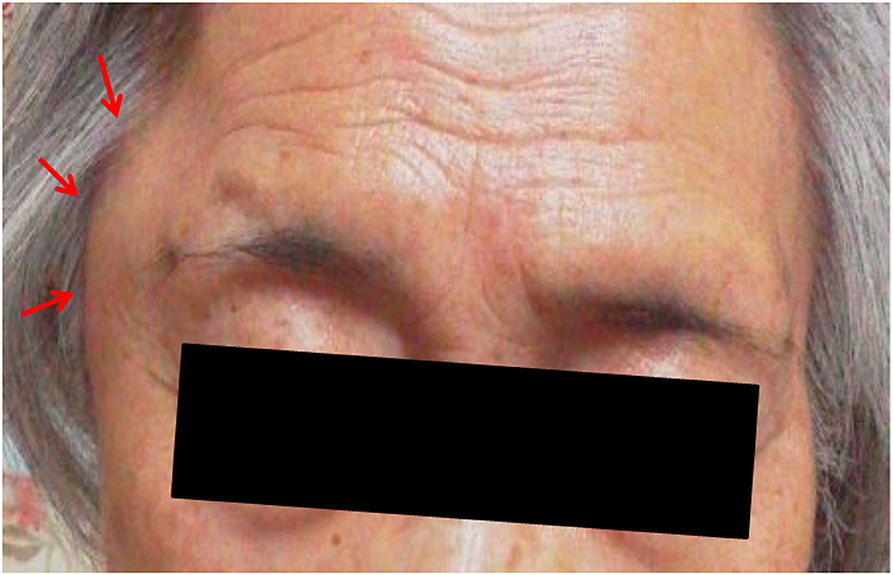




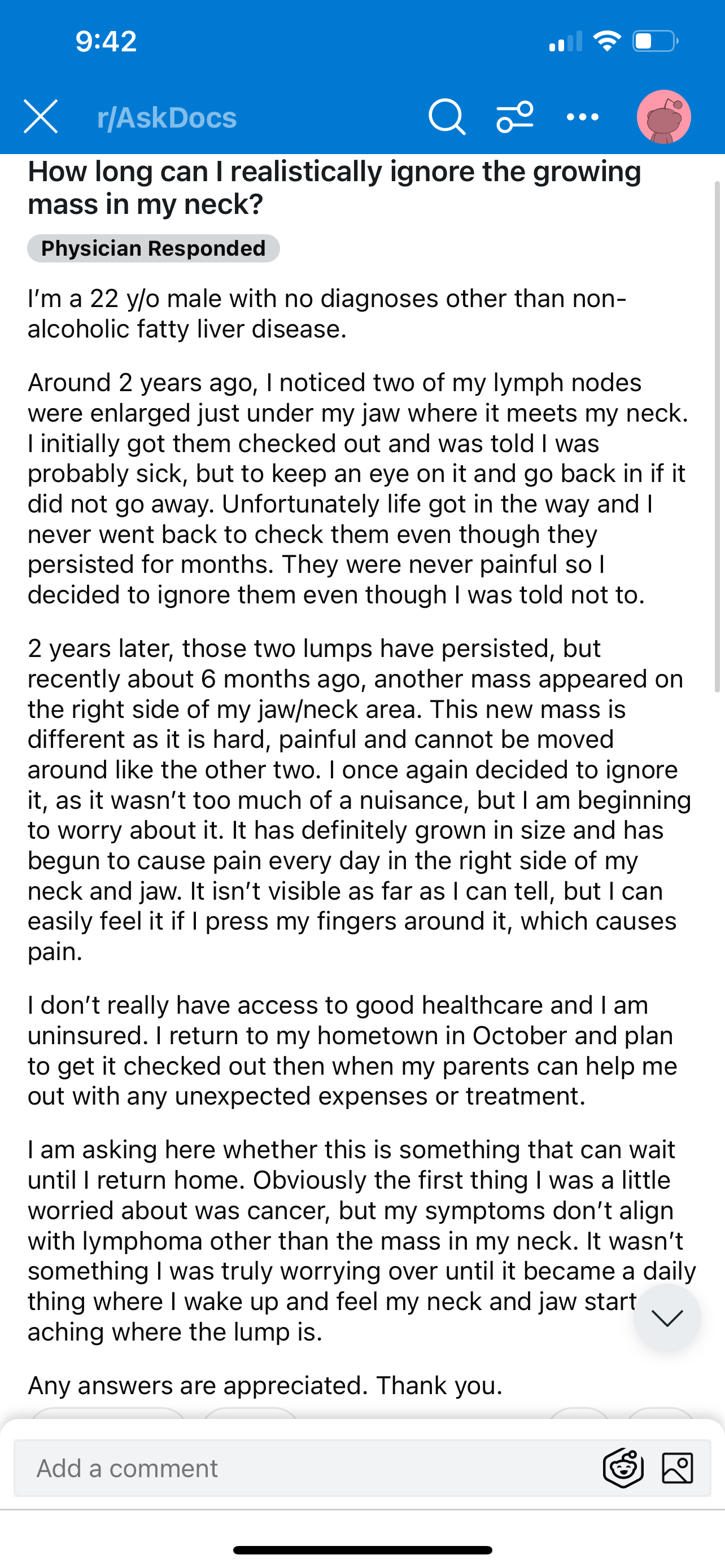
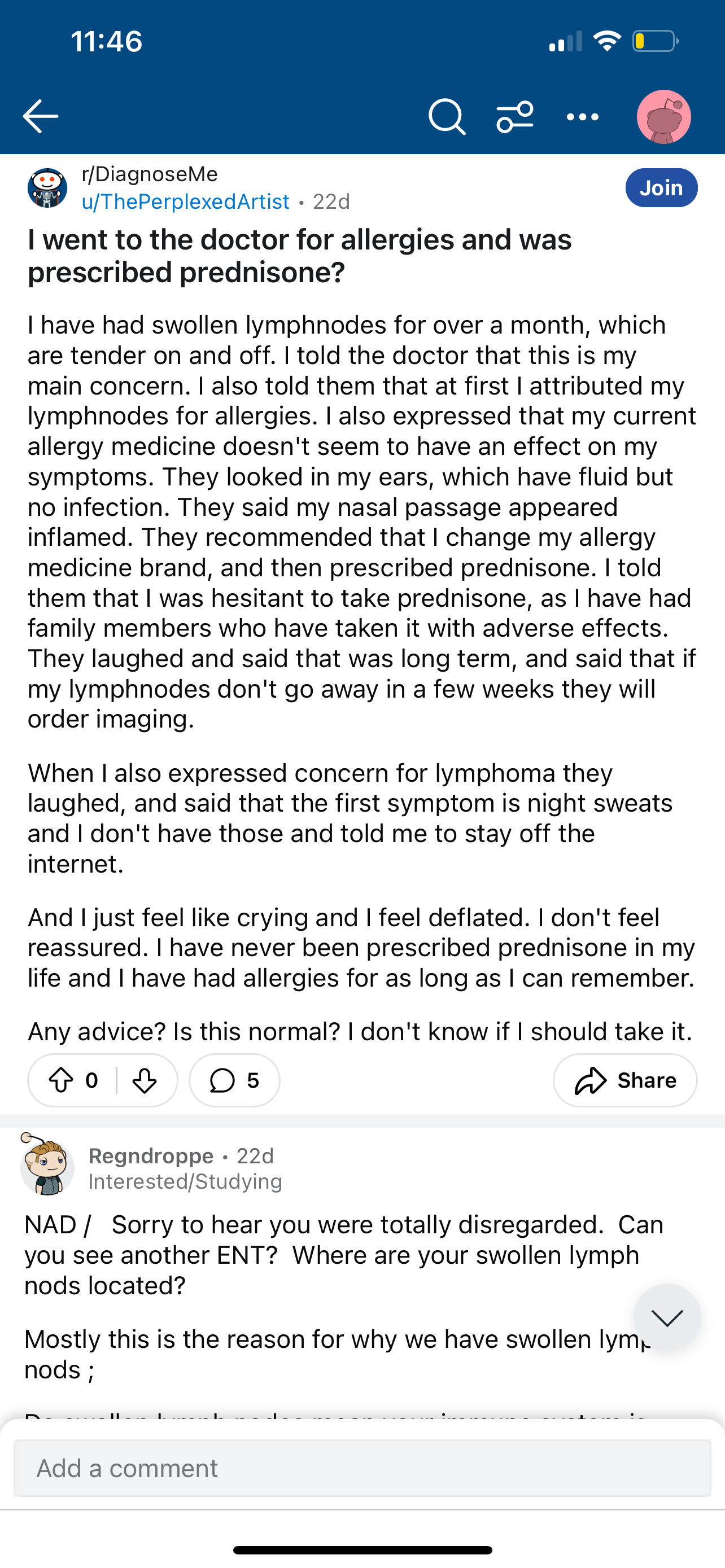
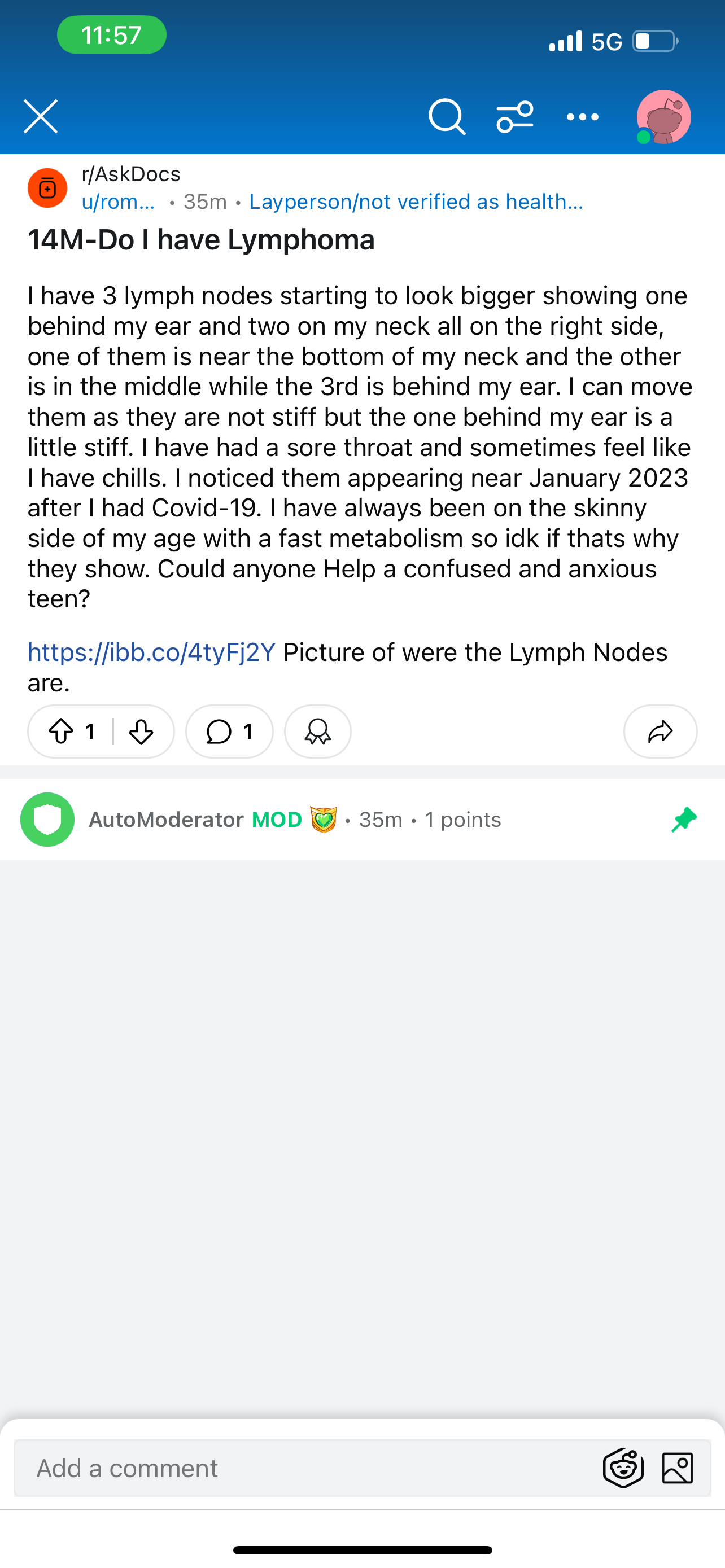
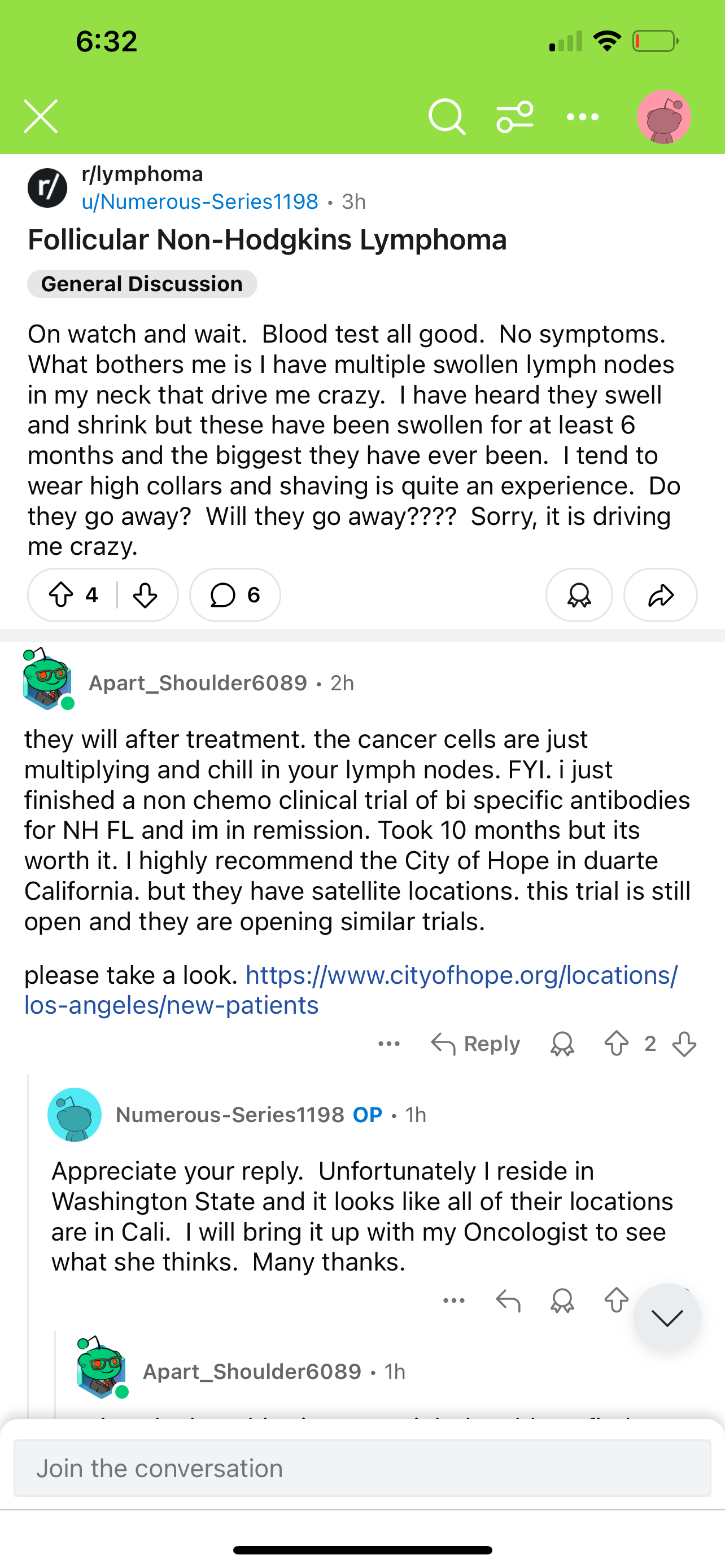
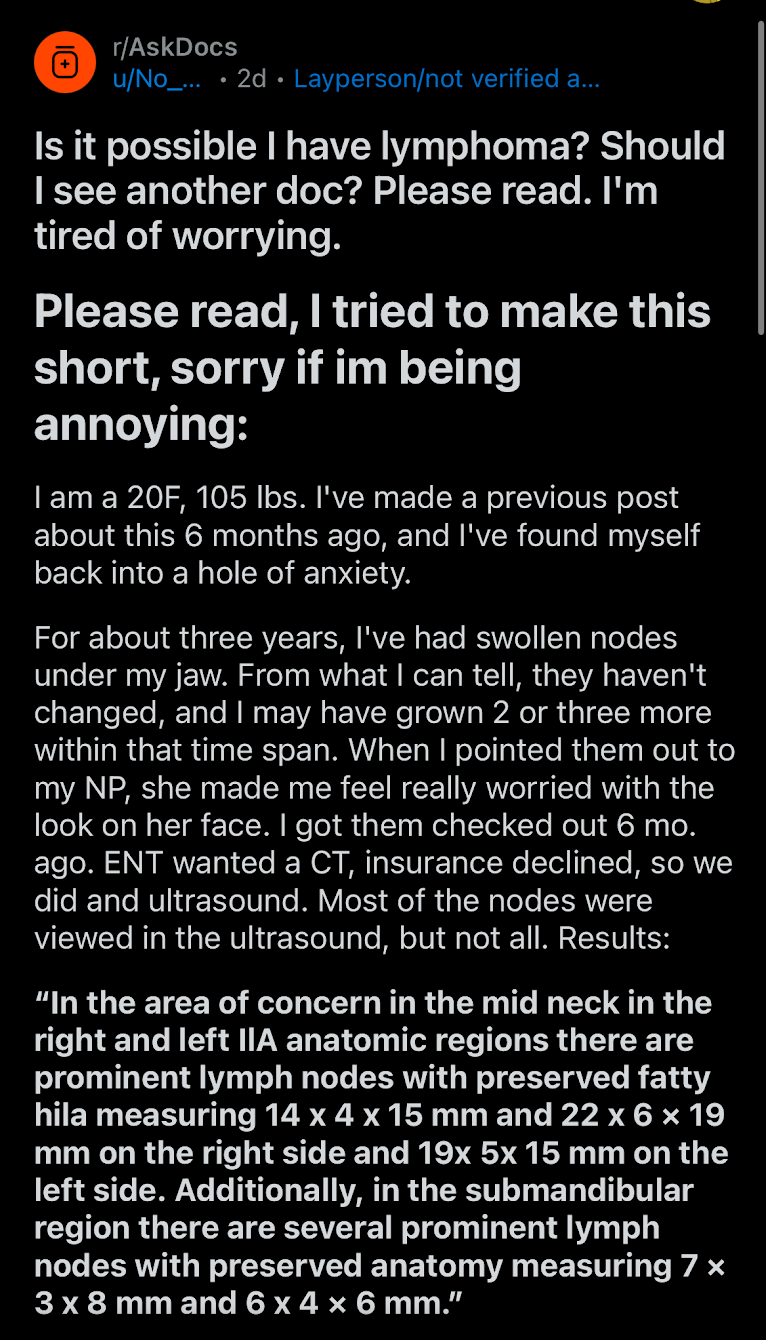
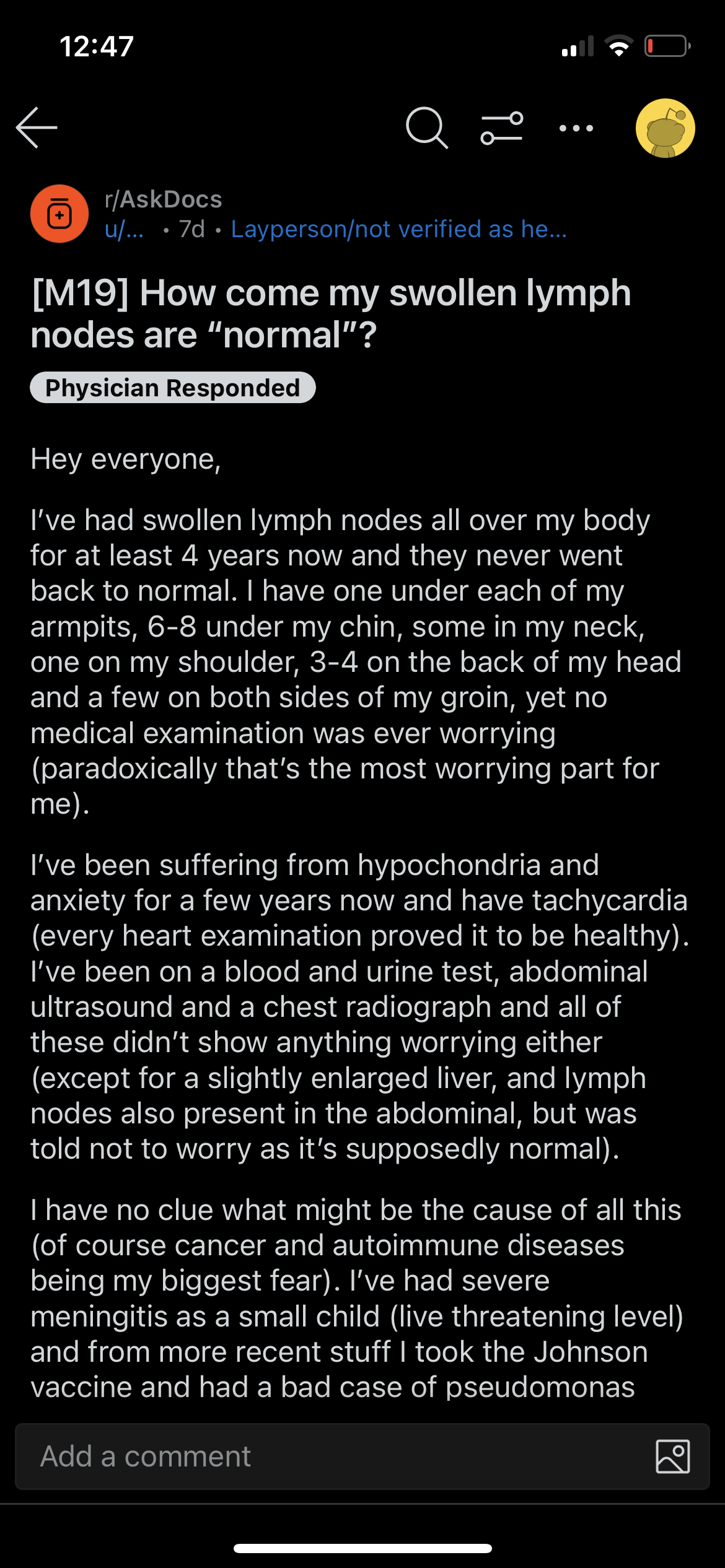
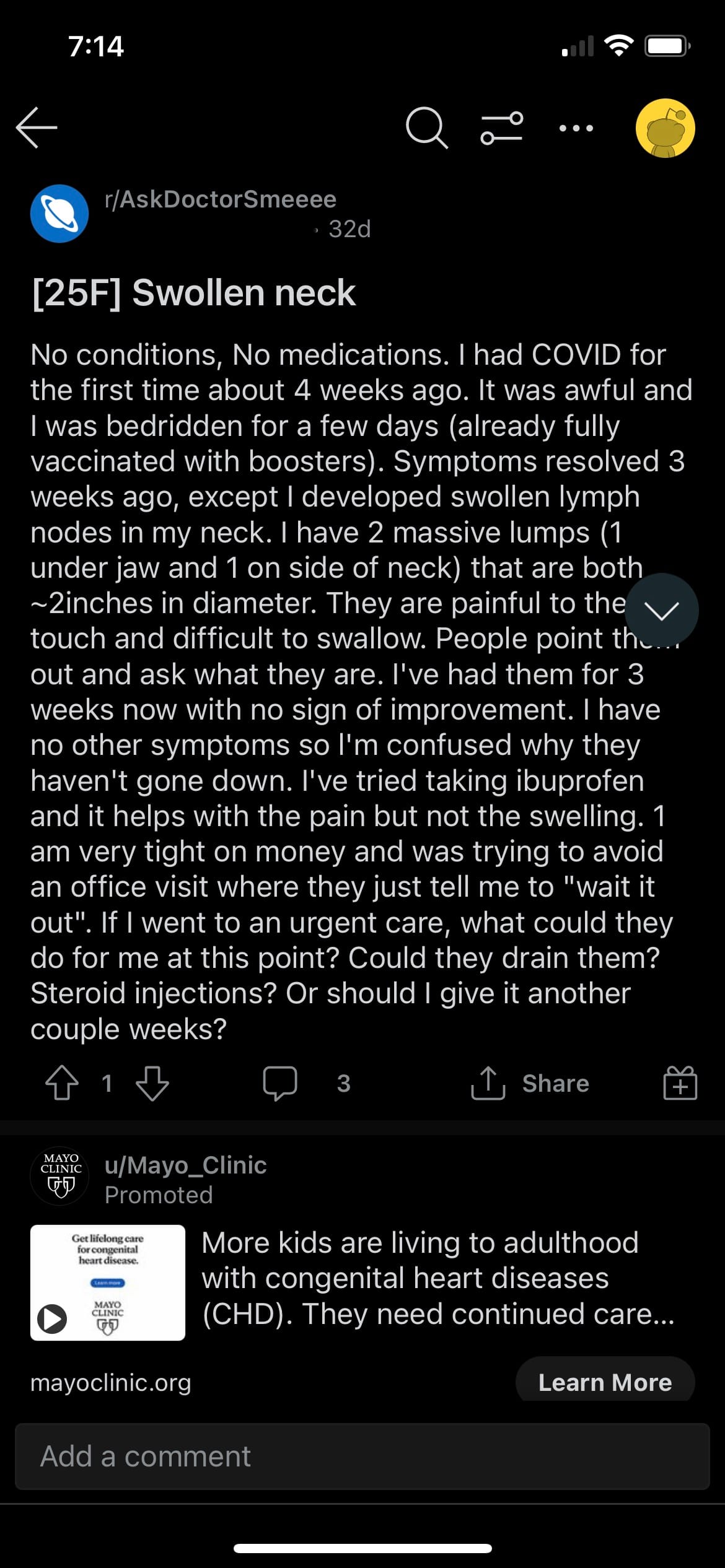
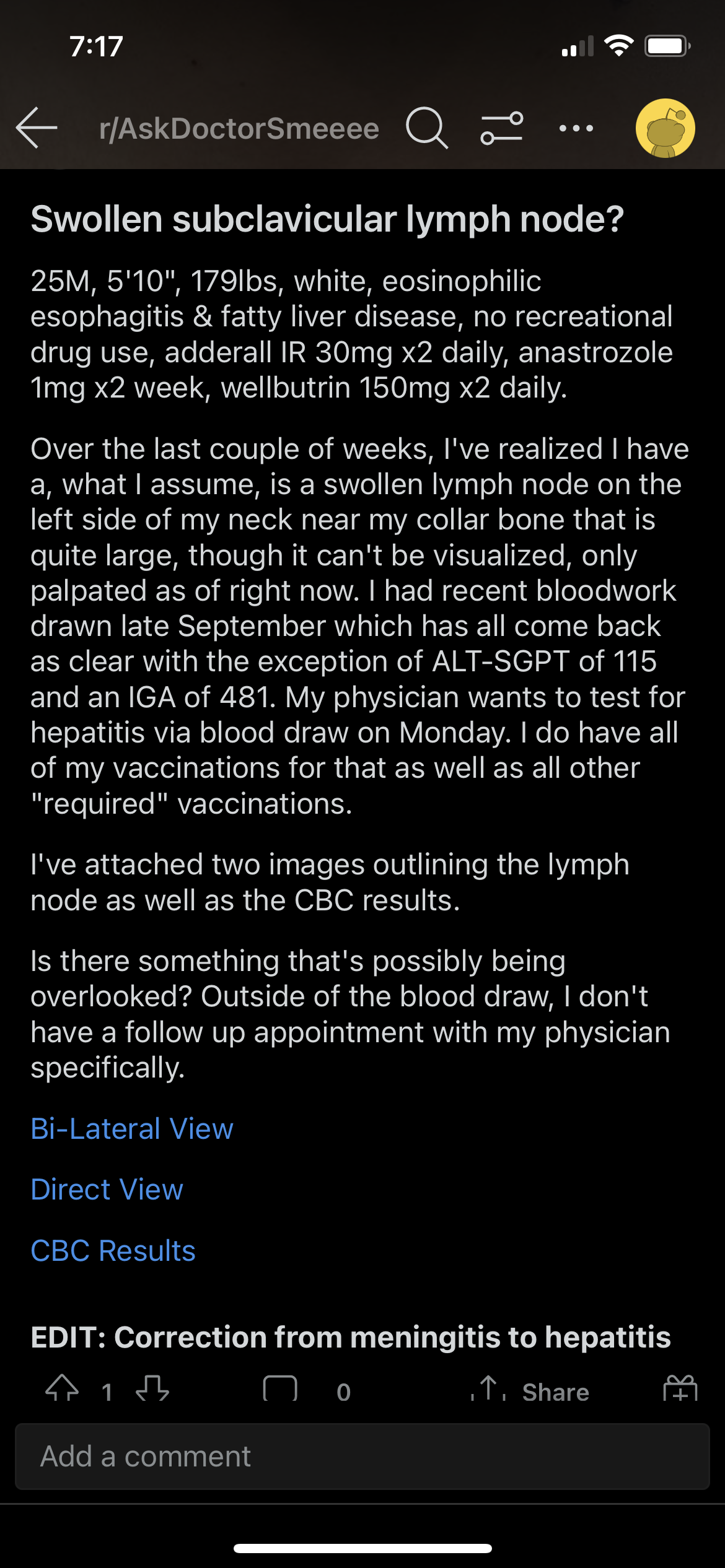
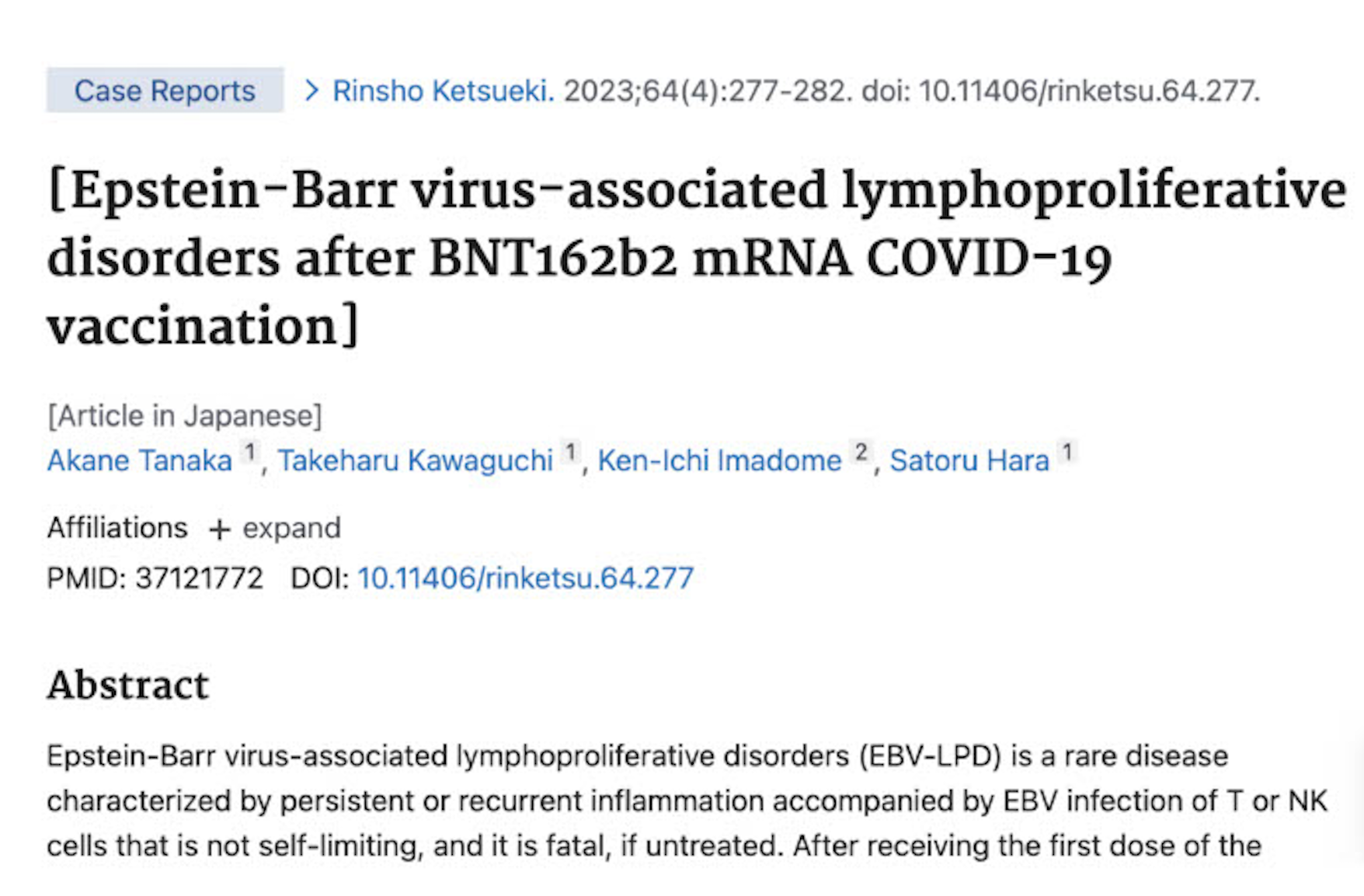

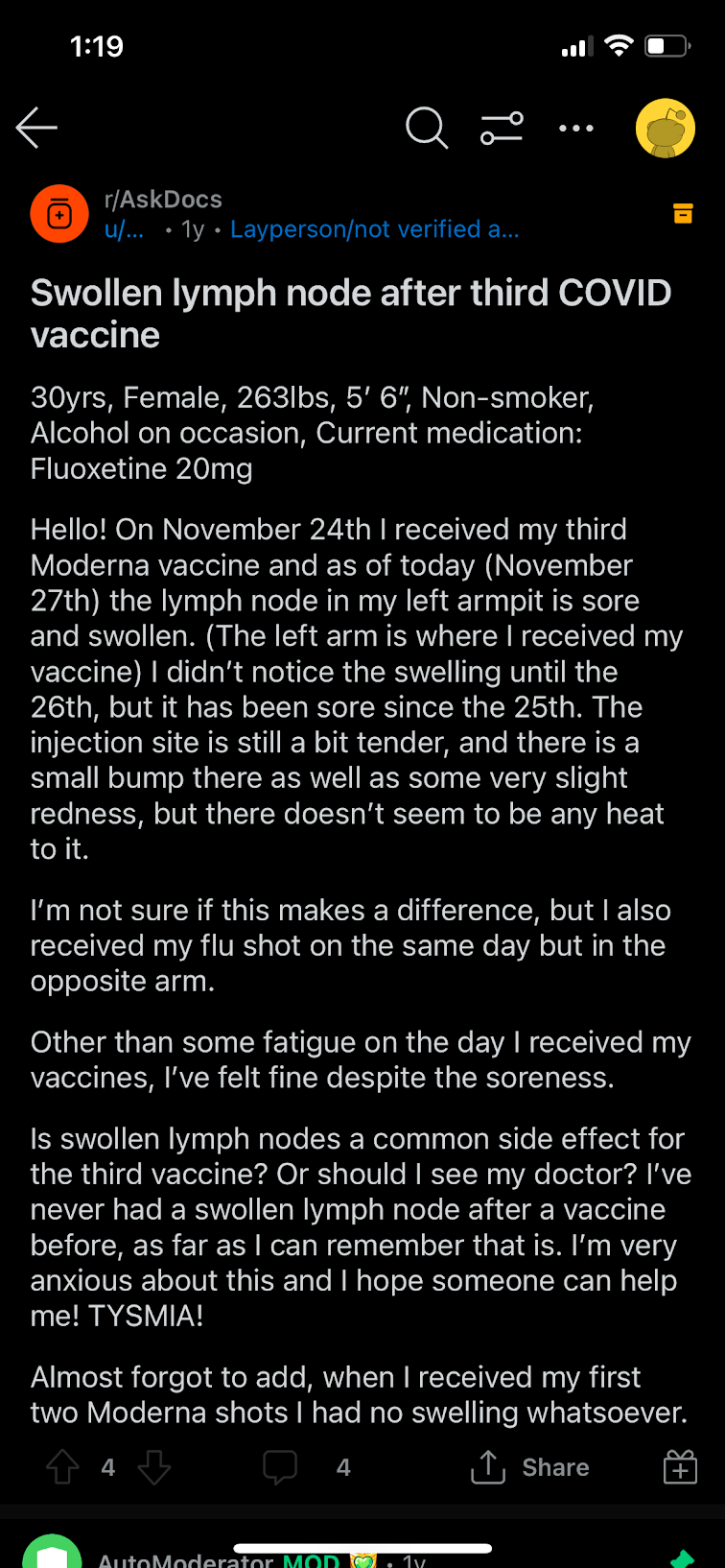
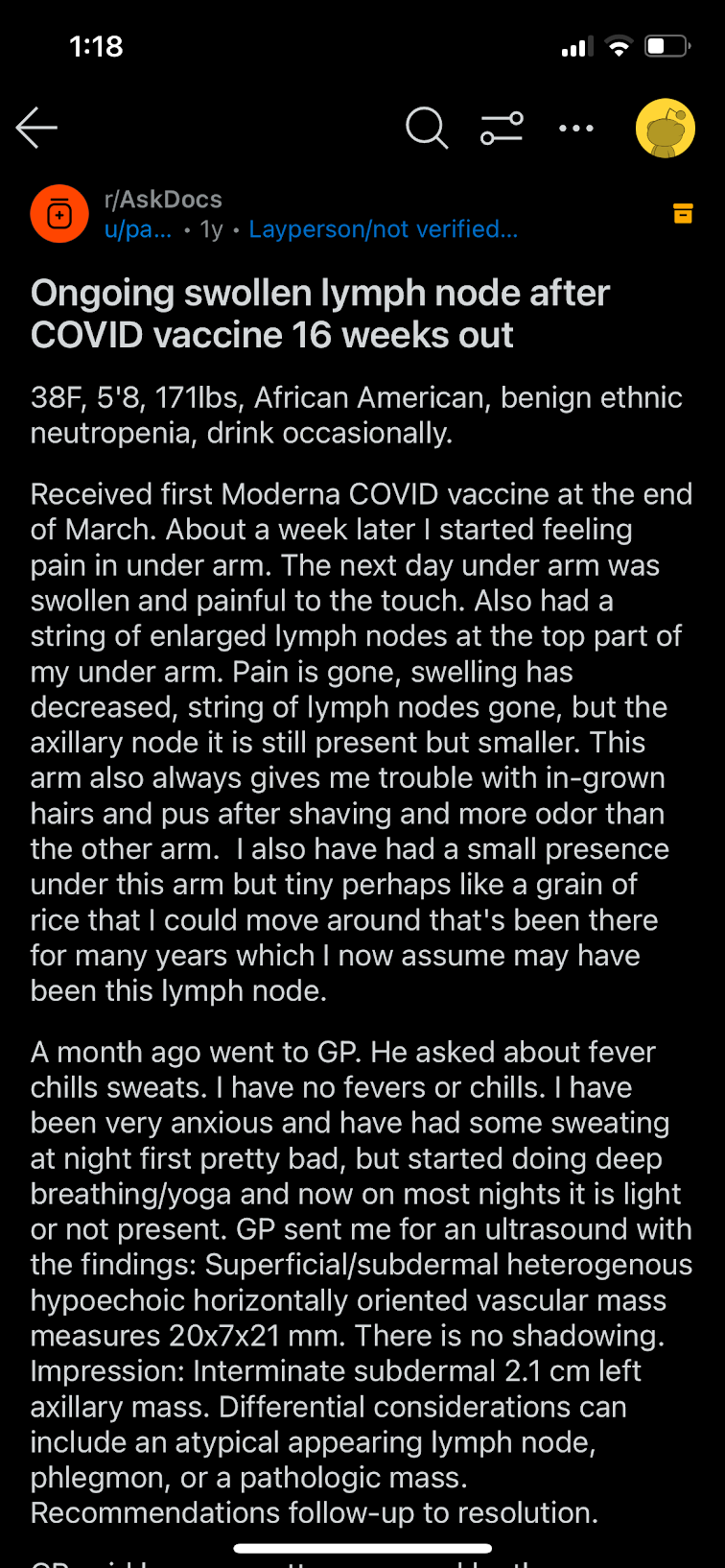
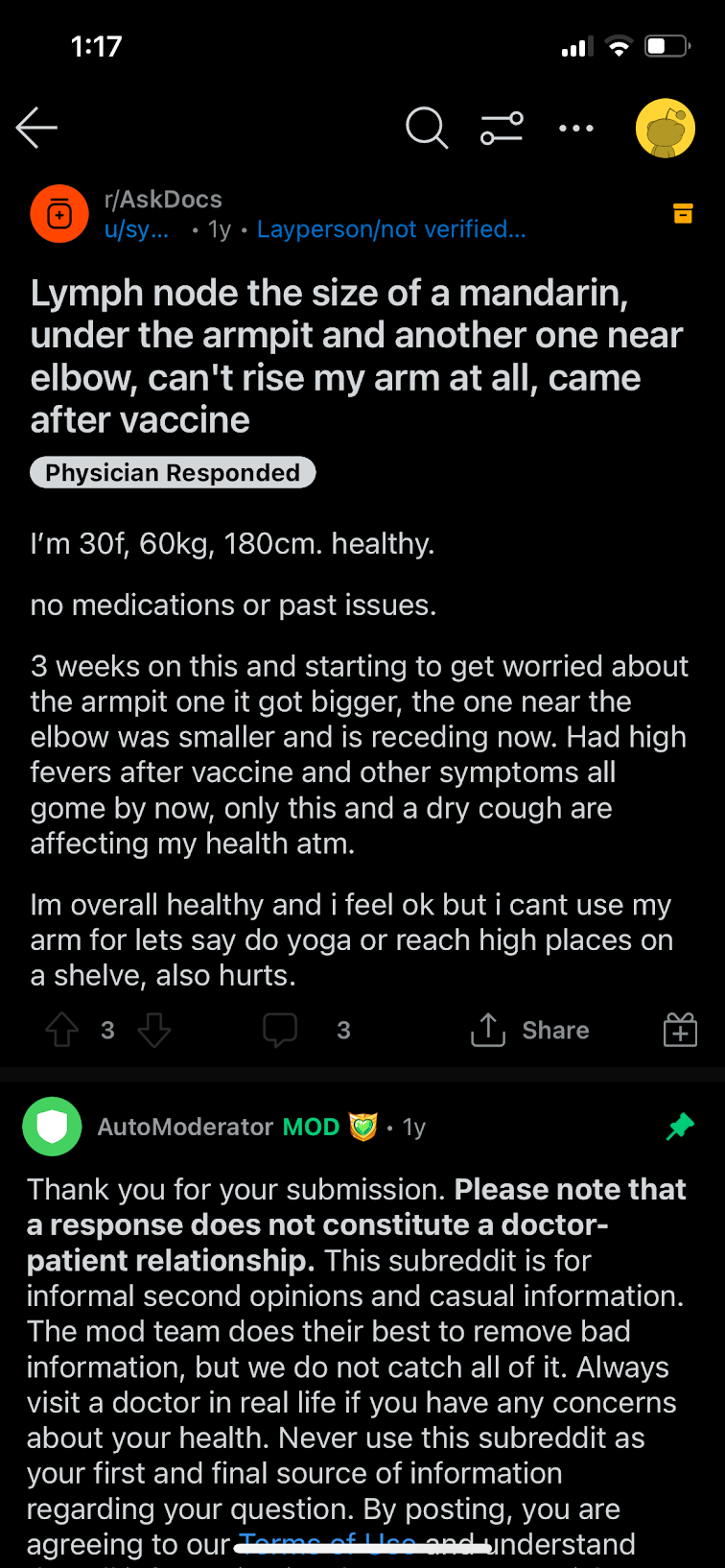
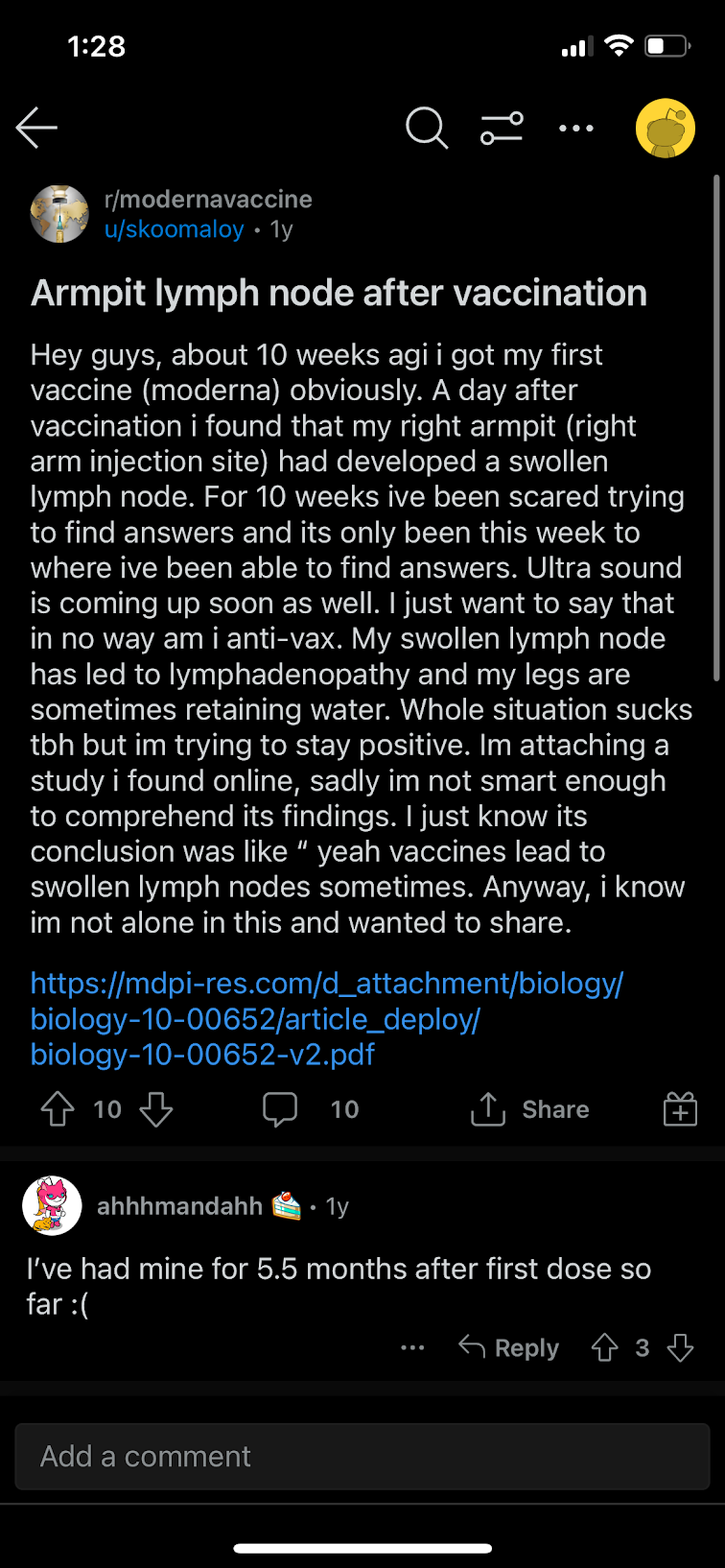
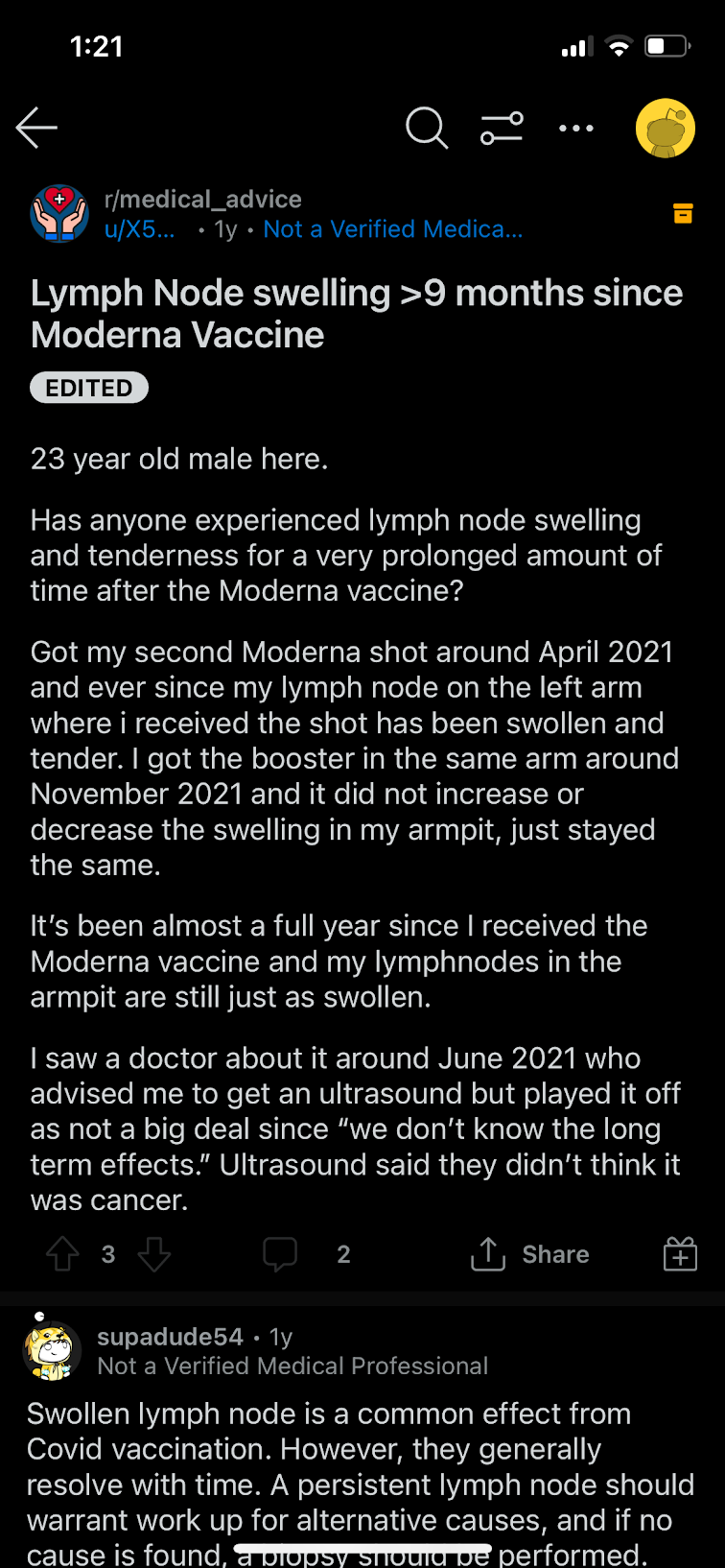
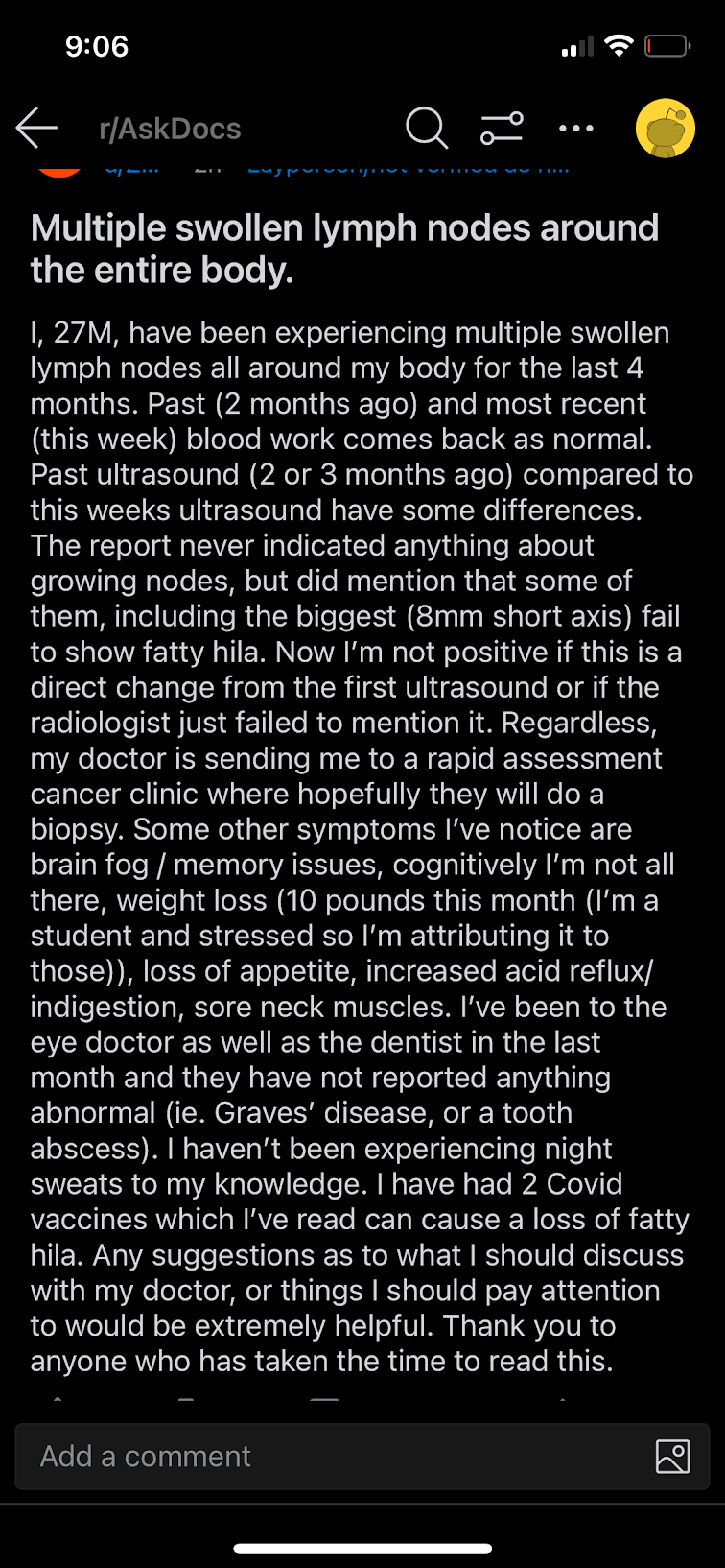
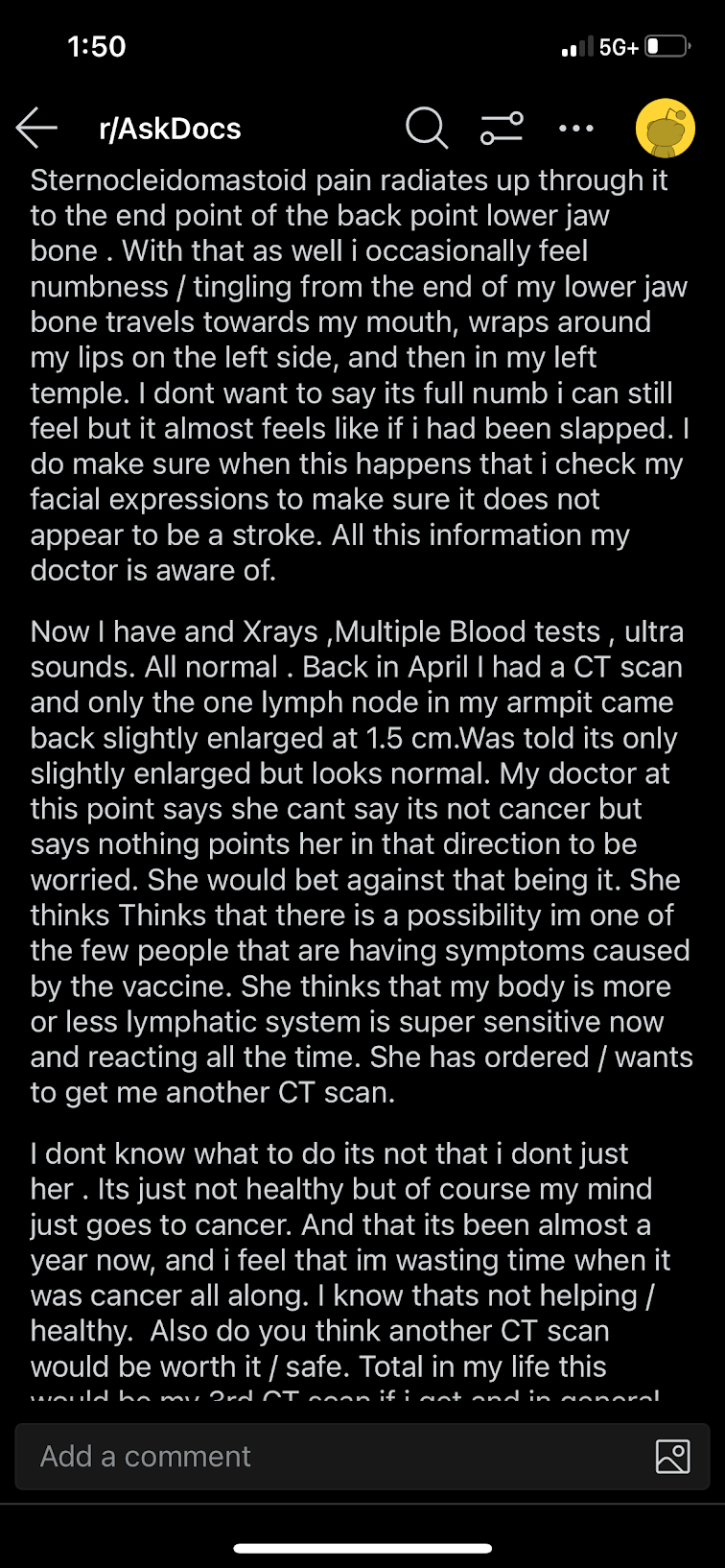
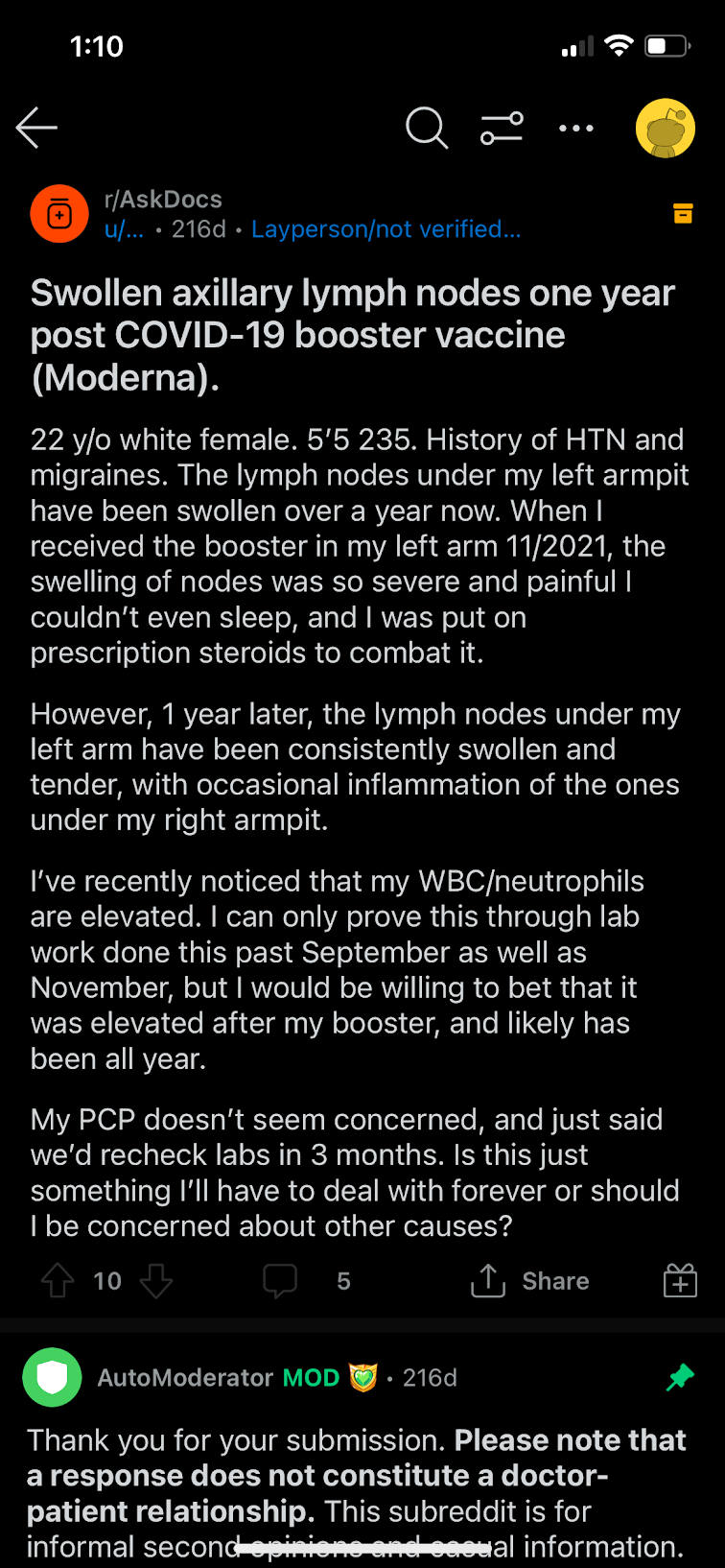
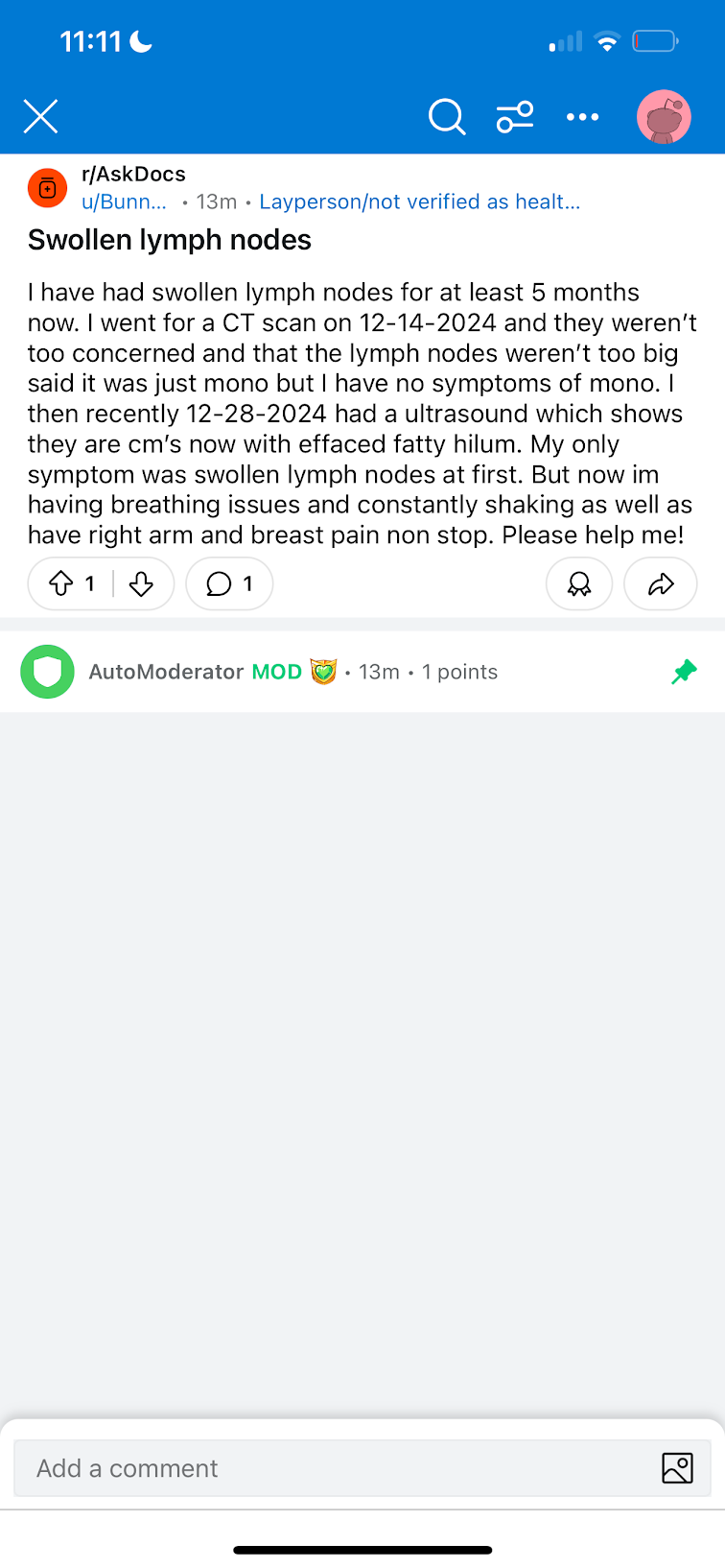
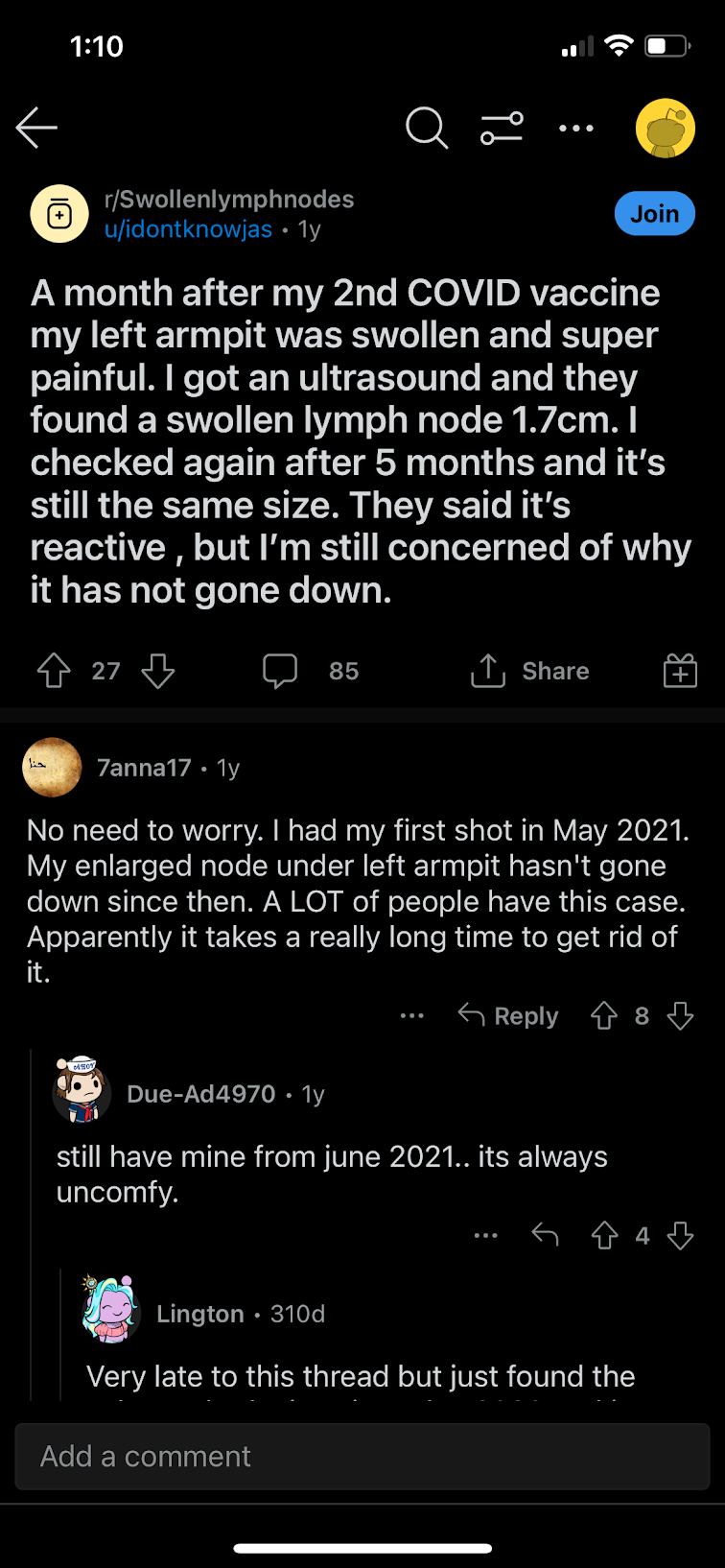
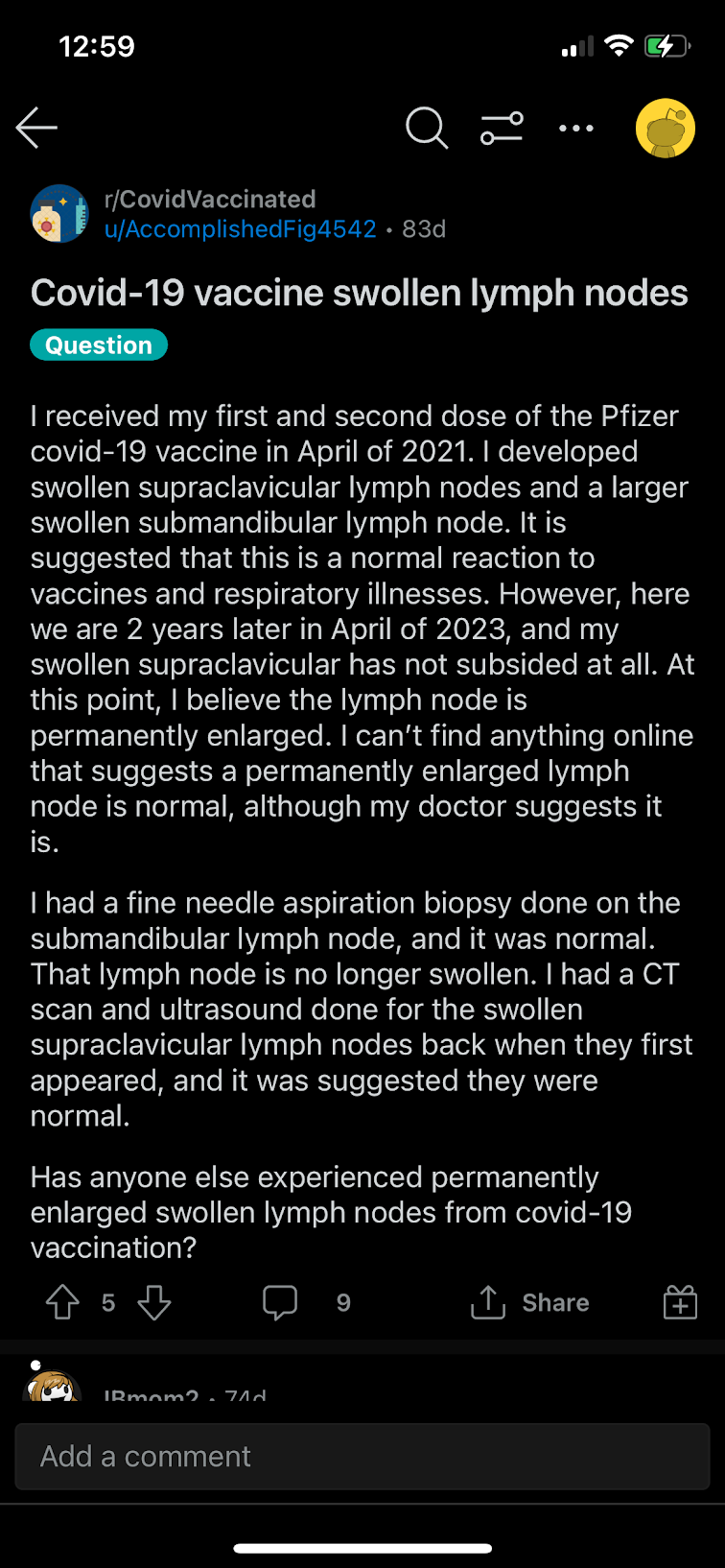
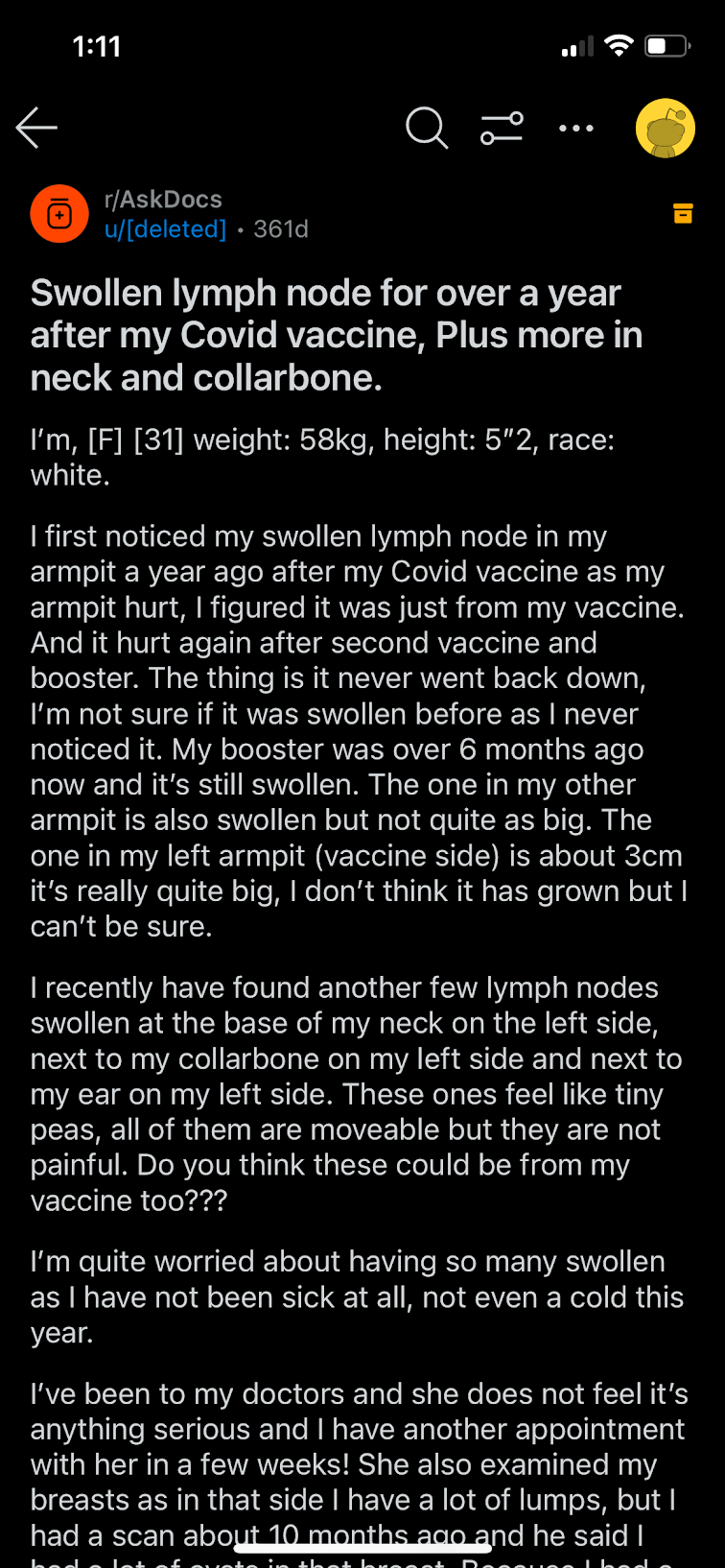
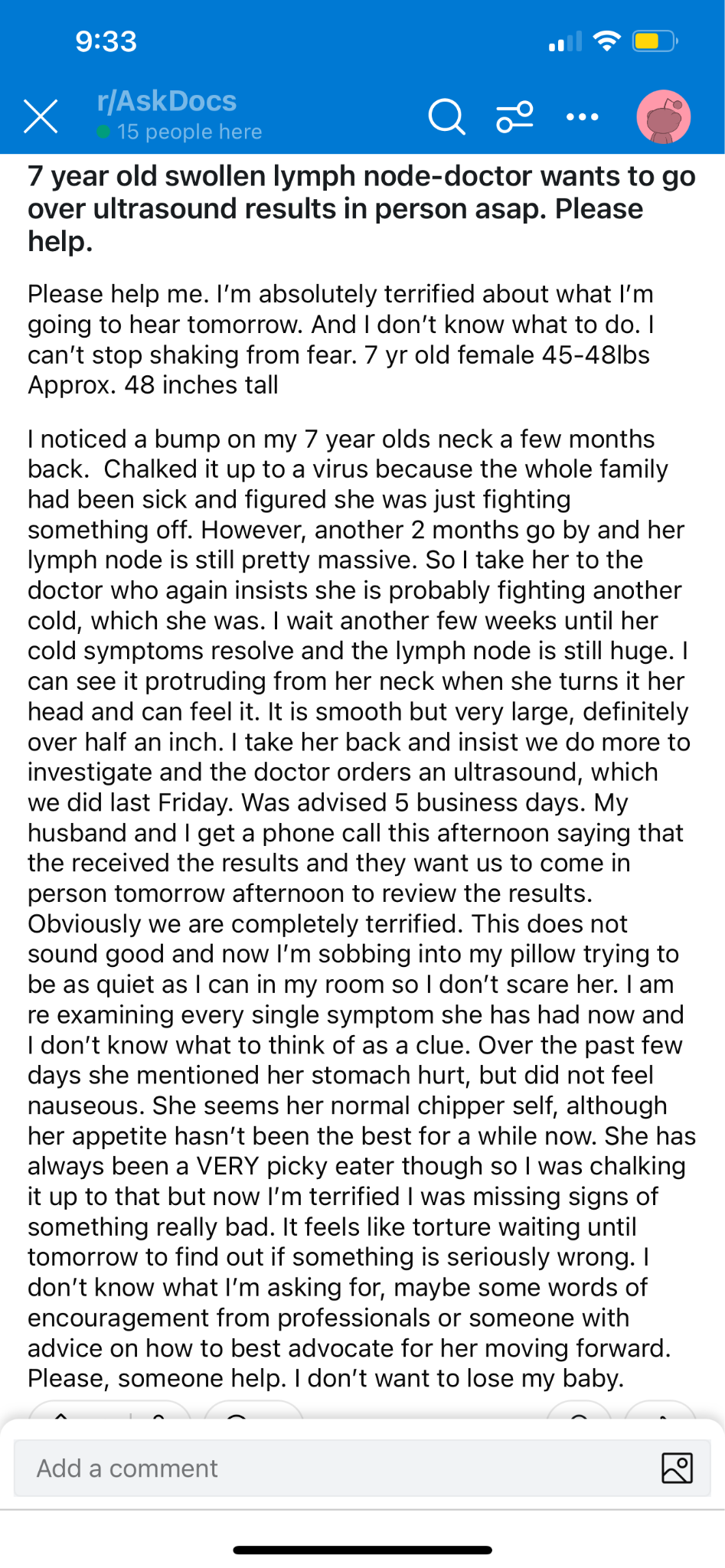














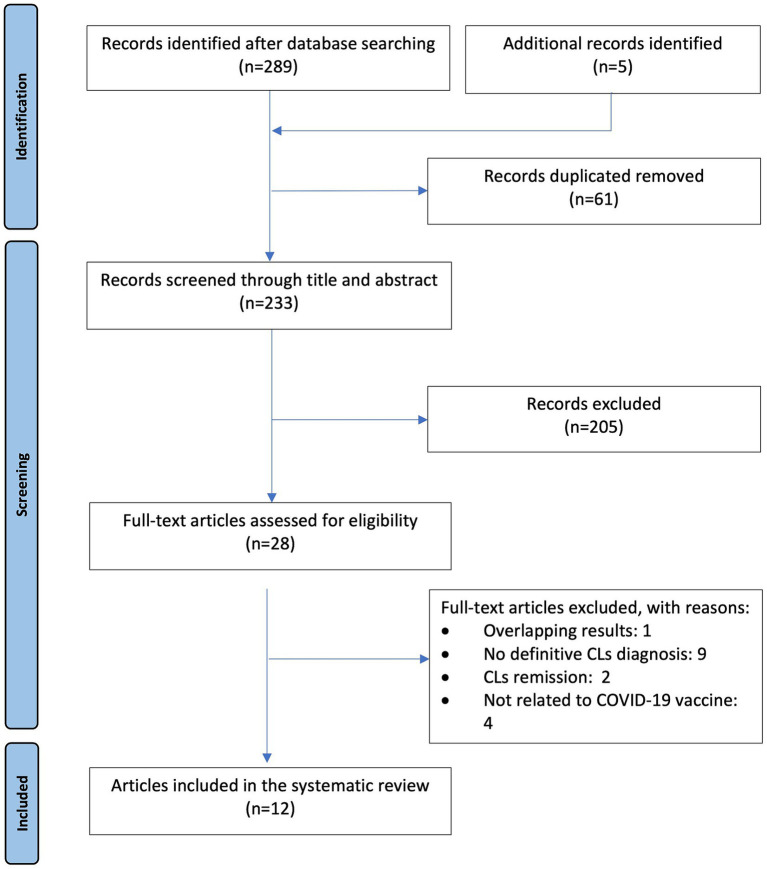
Discussion