(every point is supported by 3 to 5 screenshots from studies included below, each screenshot links to the full study)
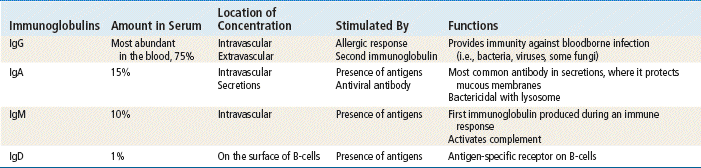
1. Antibodies ≠ Immunity
a. Historical sources (e.g., Downie 1951) and modern literature both admit that neutralizing antibodies do not correlate with protection - and never have. Yet antibody levels are what have been used to license all vaccines.
b. The WHO itself clarified that “correlates of protection” like antibody levels are not sufficient to predict immunity for most vaccines.
2. Chronically Elevated Antibodies = Risk
a. Persistent antibody stimulation is associated with allergy, autoimmunity, and systemic inflammation (Rose et al., 2015; Shoenfeld, 2011).
b. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, and autoimmune thyroiditis are marked by elevated autoreactive antibodies—suggesting the immune system’s balance is key, not mere activity.
3. Intramuscular Injection = Immunological Displacement
a. IM delivery does not mimic the natural route of pathogen exposure.
b. It bypasses the mucosal immune system (IgA-dominated) and innate pattern recognition mechanisms (via toll-like receptors), inducing immune activity in lymphoid tissue not usually exposed to environmental antigens.
c. This may increase the risk of inappropriate immune memory, especially in infants.
4. Vaccinal Immunity = Short-Term
a. Lifelong immunity from natural infection (e.g., measles, mumps, varicella) is often replaced with temporary immunity from vaccines requiring regular boosters.
b. CDC schedules now include over 70 doses by adulthood, indicating reliance on non-durable protection.
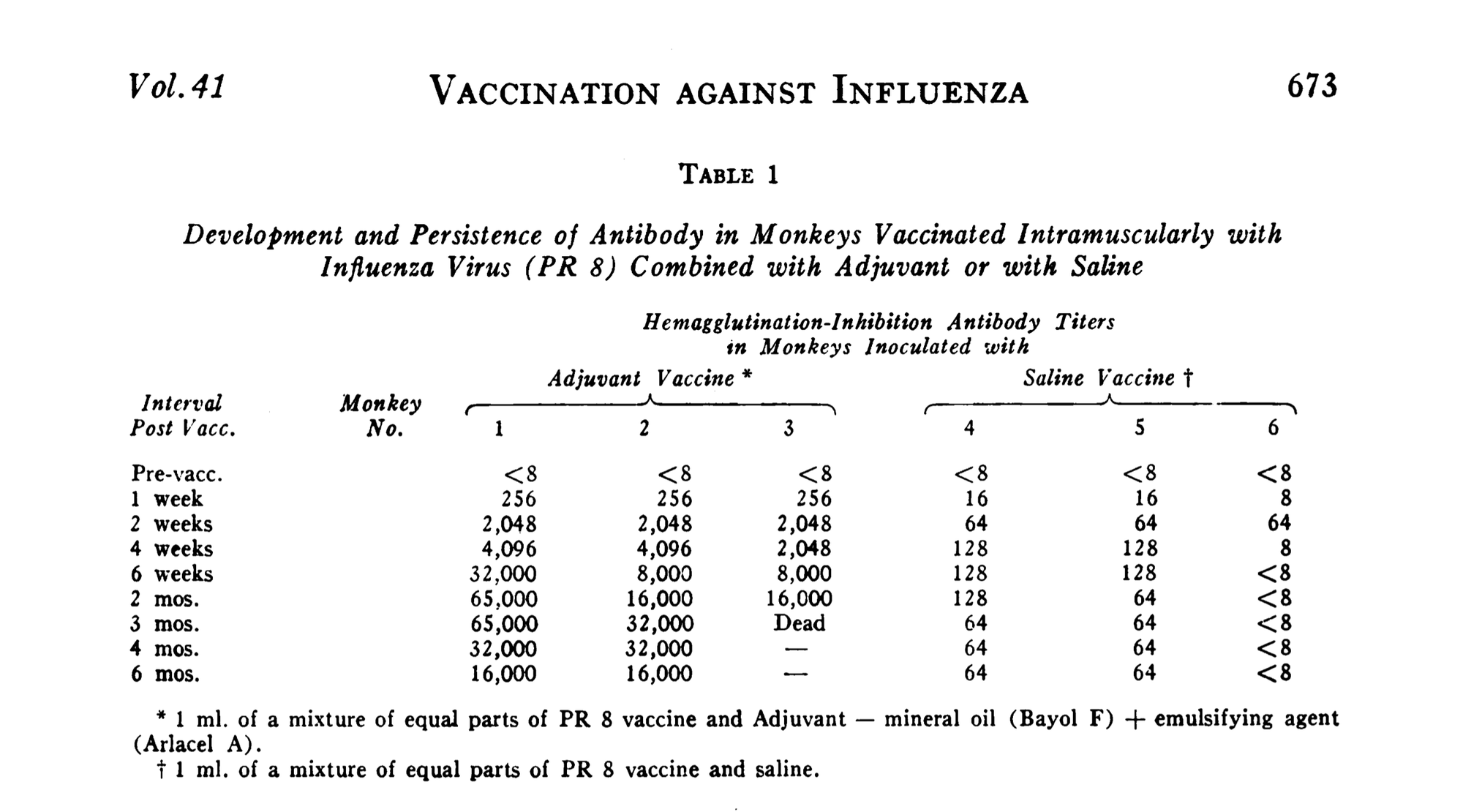
5. Adjuvants = Bioactive Persistence
a. Aluminum salts, used as adjuvants, are known to persist in macrophages and can translocate to brain tissue (e.g., Gherardi et al., 2015; Mold et al., 2014).
b. Unlike nutrients, adjuvants are not metabolized or expelled efficiently, and their long-term neuroimmune impacts remain under-studied.
6. Fever and Acute Sickness = Functional Biology
a. Fever and inflammation are part of immune training and repair.
b. Febrile illness often leads to more durable immune memory than subclinical infection or suppressed febrile responses (Kluger, 1991).
c. Suppressing illness removes a vital component of immune calibration.
7. Adverse Events = Underreported Systemic Risk
a.VAERS, a passive system, has been shown to capture less than 1% of adverse events (Harvard Pilgrim Study, 2010).
b. IOM and JAMA (1994) reports acknowledged causal links between vaccines and serious adverse outcomes like Guillain-Barré, thrombocytopenia, and anaphylaxis.
8. Long-Term Safety = Unmeasured Variable
a. Vaccine trials are typically short (6 weeks to 6 months), and long-term population-level monitoring is absent.
b. Trials rarely use inert placebos, confounding safety data.
c. Chronic disease endpoints, like autoimmunity, fertility, neurodevelopment, are not systematically studied post-licensure.
9. Informed Consent = Systematically Eroded
a. Algorithmic censorship and professional retaliation suppress dissent and nuanced debate.
b. Without transparency, true informed consent, a principle enshrined in the Nuremberg Code and Declaration of Helsinki, is unattainable.
10. Individual Variability = Ignored
a. Genomic studies have identified specific vaccine-response polymorphisms (e.g., HLA, cytokine genes).
b. Nutritional, toxicological, and metabolic contexts further shape vaccine outcomes.
c. "One-size-fits-all” fails the bio individuality standard of personalized medicine.
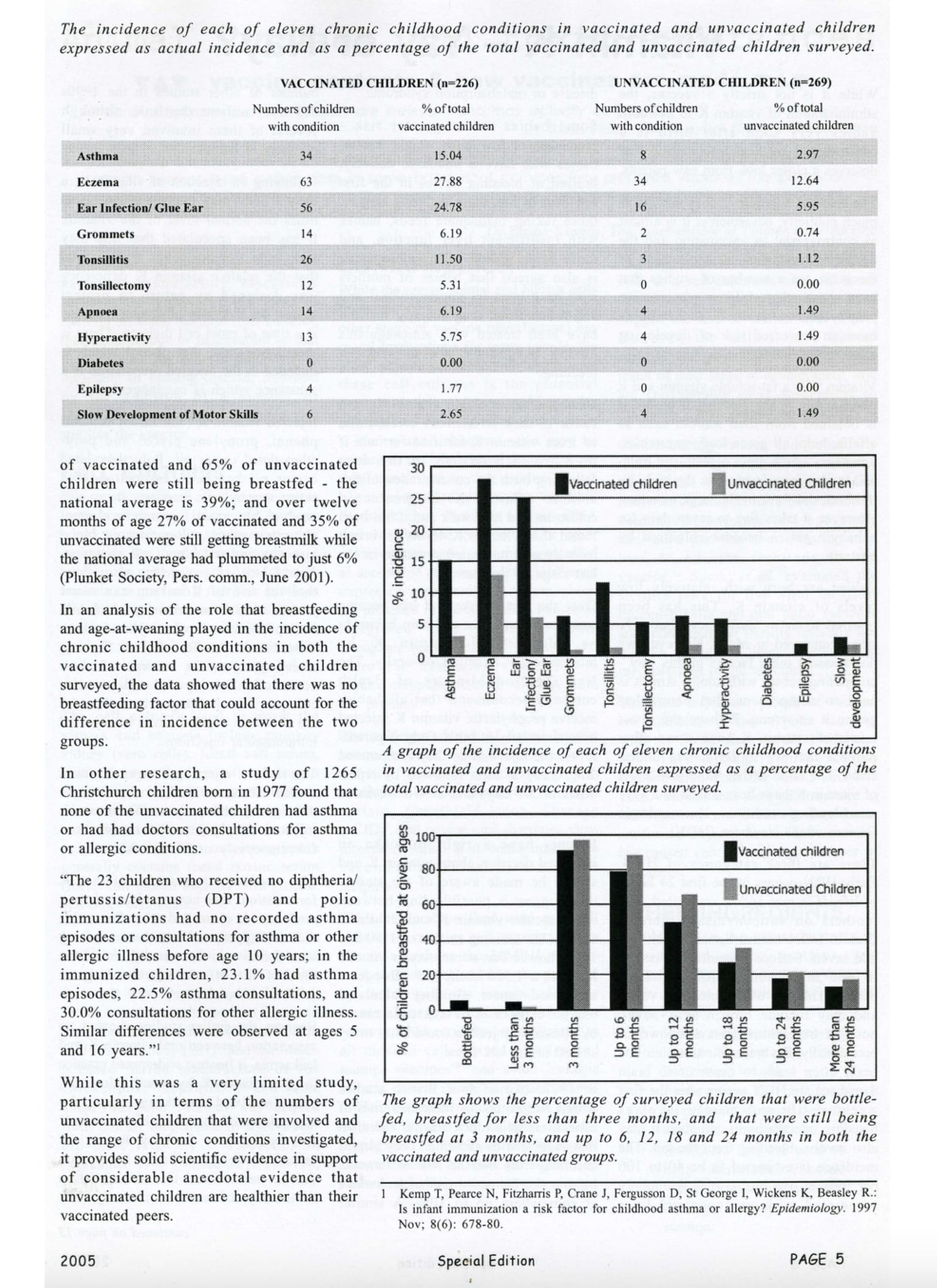
11. Chronic Illness = Possible Trade-off
a. Studies (e.g., from NZ and Germany) have shown higher incidence of asthma, eczema, and ear infections among vaccinated children, even after adjusting for confounders.
b. No definitive causation, but consistent signal across independent data sets warrants further research.
The argument is not anti-vaccine. It is pro-truth, pro-safety, and pro-individual autonomy. A science that does not question itself, that silences dissent, or that refuses to explore adverse outcomes openly has ceased to be science. It's policy disguised as medicine.
This is why the universal application of vaccination, especially in healthy, low-risk populations, should be reconsidered, not banned, but studied with a degree of honesty that current systems have failed to deliver.































the evidence


























Discussion